Runway Lighting stands as the unsung hero of aviation safety, guiding pilots through takeoffs, landings, and taxiing even when visibility plummets to near-zero. In the high-stakes world of air travel, where split-second decisions can mean the difference between safety and disaster, reliable runway lighting isn’t just a convenience—it’s a non-negotiable pillar of operational excellence. From the earliest incandescent bulbs to today’s cutting-edge LED systems paired with real-time monitoring tools, runway lighting has evolved dramatically to meet the demands of modern aviation. This blog delves into the intricacies of runway lighting—its types, functions, international standards, technological advancements, and the critical role of precision testing—proving why it remains indispensable for airports worldwide.

The Vital Importance of Runway Lighting in Aviation
Aviation safety hinges on clarity—clarity of navigation, clarity of surroundings, and clarity of decision-making—and runway lighting delivers exactly that. For pilots, especially during nighttime operations or low-visibility conditions like fog, rain, snow, or haze, runway lighting serves as a visual lifeline. It transforms an otherwise indistinct airfield into a well-defined path, ensuring aircraft stay within safe boundaries and align correctly with runways and taxiways.
The benefits of robust runway lighting extend far beyond basic visibility. First and foremost, it enhances safety by minimizing the risk of runway incursions—one of the most dangerous aviation incidents. When runways, taxiways, and their boundaries are clearly illuminated, pilots and ground personnel can easily distinguish between active flight areas and non-operational zones, reducing the chance of collisions between aircraft, vehicles, or pedestrians. Additionally, well-lit runways boost operational efficiency: airports can maintain consistent flight schedules even in challenging weather, avoiding costly delays and cancellations that disrupt travel plans and airline operations.
For commercial airlines, general aviation, and military aircraft alike, runway lighting is a universal necessity. A study by the International Air Transport Association (IATA) found that airports with state-of-the-art runway lighting systems experience 35% fewer weather-related delays and a 40% reduction in minor navigational errors during takeoff and landing. This isn’t just a statistic—it’s a testament to how runway lighting directly impacts operational reliability and passenger confidence.
Moreover, runway lighting plays a critical role in pilot situational awareness. During the final approach phase, when aircraft are descending rapidly, pilots rely on specific lighting cues to judge altitude, distance from the runway threshold, and alignment. Without these visual references, even the most experienced pilots would struggle to execute a safe landing. For example, touchdown zone lights signal the optimal point for aircraft to make contact with the runway, while centerline lights ensure the plane stays on course, preventing veering into grassy areas or other unsafe zones.

A Deep Dive into Runway Lighting Types & Their Functions
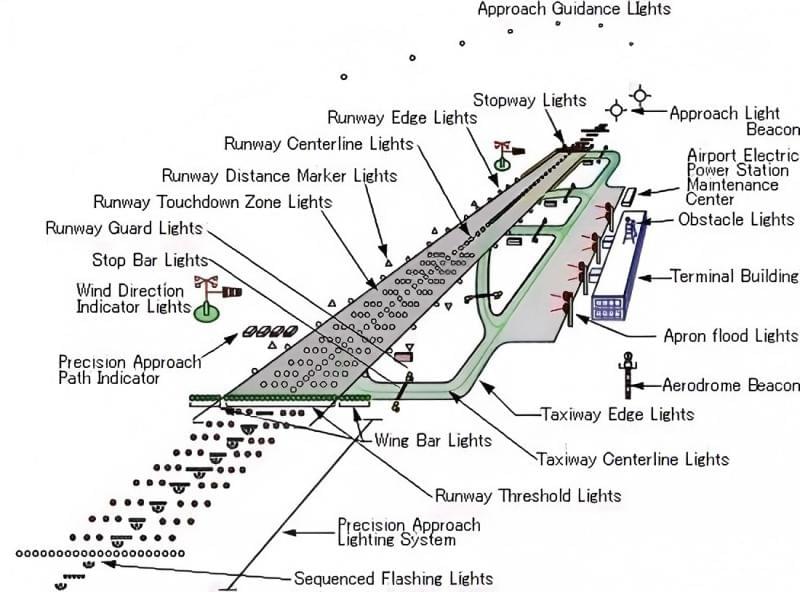
Runway lighting isn’t a one-size-fits-all system—it’s a carefully engineered network of lights, each designed to serve a specific purpose. From marking runway edges to guiding aircraft during taxiing, every component works in harmony to create a comprehensive visual guidance system. Below is a detailed breakdown of the key runway lighting types and their critical functions:
1. Runway Edge Lights
Runway edge lights are the backbone of runway visibility, marking the lateral boundaries of the runway surface. Typically installed along both sides of the runway at regular intervals (usually 50 to 200 feet apart, depending on airport size), these lights ensure pilots can clearly identify the width of the runway during approach, takeoff, and taxiing. Edge lights are available in two primary configurations: low-intensity (for small airports or visual flight rules, VFR) and high-intensity (for large commercial airports or instrument flight rules, IFR).
Most modern edge lights use LED technology, which offers superior energy efficiency, longer lifespan, and brighter illumination compared to traditional incandescent bulbs. They emit a steady white light for the runway’s length, except for the last 2,000 feet of the runway, where they switch to red to alert pilots that they’re approaching the runway end. This color transition is a critical safety feature, preventing pilots from overshooting the runway during landing or takeoff.
2. Runway Centerline Lights
Runway centerline lights are installed along the longitudinal center of the runway, providing pilots with a clear reference to maintain alignment during takeoff and landing. These lights are especially crucial in low-visibility conditions, where the runway surface may blend into the surrounding environment. Centerline lights are spaced 50 feet apart and emit a steady white light for most of the runway’s length. In the final 1,000 feet (the touchdown zone), they alternate between white and red, and in the last 500 feet, they turn fully red—signaling to pilots that they’re near the end of the runway.
For airports that handle large commercial aircraft, centerline lights are often paired with touchdown zone centerline lights, which are brighter and more concentrated to guide pilots during the critical moments of touchdown. This combination ensures that even in heavy rain or fog, pilots can stay perfectly aligned with the runway’s center, reducing the risk of lateral deviations that could lead to accidents.
3. Touchdown Zone Lights (TDZL)
Touchdown zone lights are located in the first 3,000 feet of the runway (or the first half of the runway, whichever is shorter) and are designed to help pilots identify the optimal touchdown point. These lights are arranged in two parallel rows on either side of the centerline, emitting a bright white light that’s visible from miles away. TDZLs are particularly important for IFR operations, where pilots may not have a clear view of the runway surface until the final moments of landing.
By illuminating the touchdown zone, these lights help pilots judge their descent rate and ensure they land within the safe landing area. For example, if a pilot sees the TDZLs appearing too high or too low in their field of view, they can adjust their altitude accordingly to avoid a hard landing or a landing beyond the recommended zone.
4. Runway End Identifier Lights (REIL)
Runway End Identifier Lights (REILs) are a critical component of runway lighting systems, especially for airports with challenging approach paths or frequent low-visibility conditions. Located at the approach end of the runway (one on each side of the threshold), REILs are synchronized flashing lights that alternate between red and white. Their primary function is to help pilots identify the runway’s approach end, even when the runway itself is obscured by fog, smoke, or darkness.
REILs are designed to be highly visible from a distance, with a flash rate of 40 to 60 flashes per minute. This distinctive flashing pattern makes them easy to distinguish from other airport lights, such as taxiway lights or obstacle lights. For pilots navigating through low-visibility conditions, REILs act as a beacon, guiding them toward the runway and ensuring they align their aircraft correctly for landing. Without REILs, many airports would be forced to close during foggy weather, disrupting air travel and causing significant economic losses.
5. Taxiway Lights
While not technically part of the runway itself, taxiway lights are an integral part of the overall airfield lighting system, working in tandem with runway lighting to guide aircraft between runways, terminals, and maintenance facilities. Taxiway lights are typically blue, making them easy to distinguish from the white and red runway lights. They include edge lights (marking the sides of taxiways), centerline lights (guiding aircraft along the taxiway’s center), and stop bar lights (signaling when an aircraft must stop before entering a runway).
Taxiway lights are low-intensity compared to runway lights, as they don’t need to be visible from high altitudes. However, they must be bright enough to be seen by pilots during nighttime or low-visibility taxiing. LED taxiway lights are now the industry standard, as they consume less energy, require less maintenance, and have a longer lifespan than traditional bulbs.
6. Obstacle Lights
Obstacle lights are installed on structures near the runway, such as trees, buildings, towers, or power lines, to warn pilots of potential hazards. These lights are typically red or white and may be steady or flashing, depending on the height and location of the obstacle. For example, tall structures (over 200 feet) use flashing red lights, while shorter obstacles use steady red or white lights.
Obstacle lights are a critical safety feature, as they prevent pilots from colliding with objects that could interfere with takeoff or landing. They are especially important during nighttime operations, when obstacles are less visible to the naked eye. Airports are required by international regulations to maintain obstacle lights in good working order, as any malfunction could pose a significant risk to flight safety.
International Standards for Runway Lighting: Ensuring Global Consistency
Aviation is a global industry, and consistency in safety standards is paramount. To ensure that runway lighting systems meet uniform requirements worldwide, the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) has established strict regulations regarding the color, intensity, placement, and functionality of runway lights. These standards are designed to eliminate confusion among pilots, regardless of which airport they’re operating from, and to ensure that runway lighting works in harmony with aircraft navigation lights.
Key ICAO Regulations for Runway Lighting
1.Color Specifications: ICAO mandates specific colors for different types of runway lights to ensure clarity and avoid misinterpretation. For example:
- Runway edge lights: White (except for the last 2,000 feet, which are red)
- Centerline lights: White (with red transitions in the touchdown zone and runway end)
- Touchdown zone lights: White
- REILs: Alternating red and white (flashing)
- Taxiway lights: Blue
- Obstacle lights: Red or white (depending on height)
2.Intensity Requirements: Runway lights must meet minimum intensity levels to be visible in various weather conditions. ICAO classifies runway lighting into different intensity categories (Low Intensity Runway Lights, LIRL; Medium Intensity Runway Lights, MIRL; High Intensity Runway Lights, HIRL) based on the airport’s operational needs. For example, HIRL systems are required for large commercial airports with high traffic volumes and IFR operations, as they provide maximum visibility in fog, rain, and darkness.
3.Placement and Spacing: ICAO specifies exact spacing and placement for runway lights to ensure uniform coverage. For instance, edge lights must be spaced no more than 200 feet apart for HIRL systems, while centerline lights must be spaced 50 feet apart. These requirements ensure that pilots receive consistent visual cues regardless of their position relative to the runway.
4.Compatibility with Navigation Lights: ICAO regulations also ensure that runway lighting is compatible with aircraft navigation lights. Aircraft navigation lights include red wingtip lights (port side), green wingtip lights (starboard side), and white tail lights. Runway lights are designed to be distinct from these colors, preventing pilots from confusing runway lights with the navigation lights of other aircraft. This compatibility is critical during takeoff and landing, when pilots must quickly distinguish between their own aircraft’s lights, other planes, and the runway itself.
Compliance with ICAO standards is not optional—it’s a legal requirement for all airports that operate international flights. Airports that fail to meet these standards risk losing their certification, which would disrupt their operations and damage their reputation. Additionally, compliance ensures that pilots can rely on consistent visual cues, reducing the risk of human error and enhancing overall flight safety.

The Evolution of Runway Lighting Technology: From Incandescent to LED & Beyond
Runway lighting technology has come a long way since the early days of aviation, when airports relied on simple incandescent bulbs to illuminate runways. Today, advancements in LED technology, computer vision, and real-time monitoring have transformed runway lighting into a sophisticated, efficient, and reliable system. Below is a look at the key milestones in the evolution of runway lighting technology:
1. The Era of Incandescent Bulbs
In the early 20th century, runway lighting consisted of incandescent bulbs mounted on wooden poles along the runway. These bulbs were dim, energy-inefficient, and had a short lifespan (typically 1,000 to 2,000 hours). They also required frequent maintenance, as they burned out quickly and were susceptible to damage from weather and vibration. Despite these limitations, incandescent bulbs were the only option for decades, and they played a critical role in enabling nighttime flight operations.
2. The Shift to Halogen and Fluorescent Lights
In the 1960s and 1970s, airports began transitioning to halogen and fluorescent lights, which offered brighter illumination and longer lifespans than incandescent bulbs. Halogen lights, in particular, were popular for runway edge and centerline lights, as they provided a more intense white light that was visible in adverse weather. Fluorescent lights were used for taxiway lights and other low-intensity applications, as they were more energy-efficient than halogen bulbs.
However, halogen and fluorescent lights still had significant drawbacks. Halogen bulbs consumed a lot of energy and generated excessive heat, which made them prone to overheating and failure. Fluorescent bulbs, while more efficient, were fragile and could break easily during maintenance or severe weather. Additionally, both technologies required regular replacement, leading to high maintenance costs for airports.
3. The Rise of LED Runway Lights
The 21st century brought a revolution in runway lighting with the adoption of Light-Emitting Diode (LED) technology. LEDs offer a host of advantages over traditional bulbs, making them the preferred choice for modern airports:
- Energy Efficiency: LEDs consume up to 80% less energy than incandescent bulbs and 50% less than halogen bulbs, reducing airports’ energy costs significantly.
- Long Lifespan: LEDs have a lifespan of 50,000 to 100,000 hours—50 to 100 times longer than incandescent bulbs. This means fewer replacements and lower maintenance costs.
- Brightness and Visibility: LEDs emit a bright, focused light that is highly visible in low-visibility conditions. They also have a faster response time than traditional bulbs, making them ideal for flashing lights like REILs.
- Durability: LEDs are solid-state devices, meaning they have no filaments or glass components that can break. They are resistant to vibration, temperature extremes, and weather damage, making them ideal for outdoor airfield environments.
- Flexibility: LEDs can be easily dimmed or brightened to adjust to different lighting conditions, such as daytime, nighttime, or low visibility. This flexibility allows airports to optimize visibility while conserving energy.
Today, nearly all new runway lighting installations use LED technology, and many older airports are retrofitting their existing systems with LEDs. According to a report by the Airports Council International (ACI), LED runway lights can reduce an airport’s lighting-related energy costs by up to 70% and maintenance costs by up to 90%, making them a cost-effective long-term investment.
4. Cutting-Edge Advancements: Computer Vision 3D Measurement & Linear Array Scanning
While LEDs have transformed runway lighting, the latest technological advancements are taking it to the next level. Two key innovations are Computer Vision 3D Measurement and Linear Array Scanning Positioning Correction, which are revolutionizing how airports maintain and optimize their runway lighting systems.
Computer Vision 3D Measurement: This technology uses advanced cameras and software to capture detailed 3D images of runway lights and their surroundings. By analyzing these images, airport authorities can accurately assess the alignment, intensity, and condition of each light. This level of precision ensures that runway lights are functioning optimally and meeting ICAO standards. For example, if a light is misaligned or dimmer than required, the system can detect it immediately, allowing for prompt maintenance.
Computer Vision 3D Measurement also enables real-time monitoring of runway lighting systems. Airports can access data on light performance remotely, allowing them to identify issues before they impact flight operations. This proactive approach reduces the risk of unexpected failures and ensures that pilots always have clear visibility.
Linear Array Scanning Positioning Correction: This technology uses precise scanning mechanisms to ensure that each runway light is positioned correctly. By scanning the runway at regular intervals, the system can detect any shifts in light placement (caused by weather, ground movement, or maintenance) and correct them automatically. This ensures that the visual cues provided by runway lights are consistent and accurate, helping pilots maintain proper alignment during takeoff and landing.
These advancements not only enhance safety but also improve operational efficiency. By reducing the need for manual inspections and maintenance, airports can save time and resources, allowing them to focus on other critical aspects of airfield operations.
The Critical Role of Real-Time Light Intensity Testing for Runway Lighting
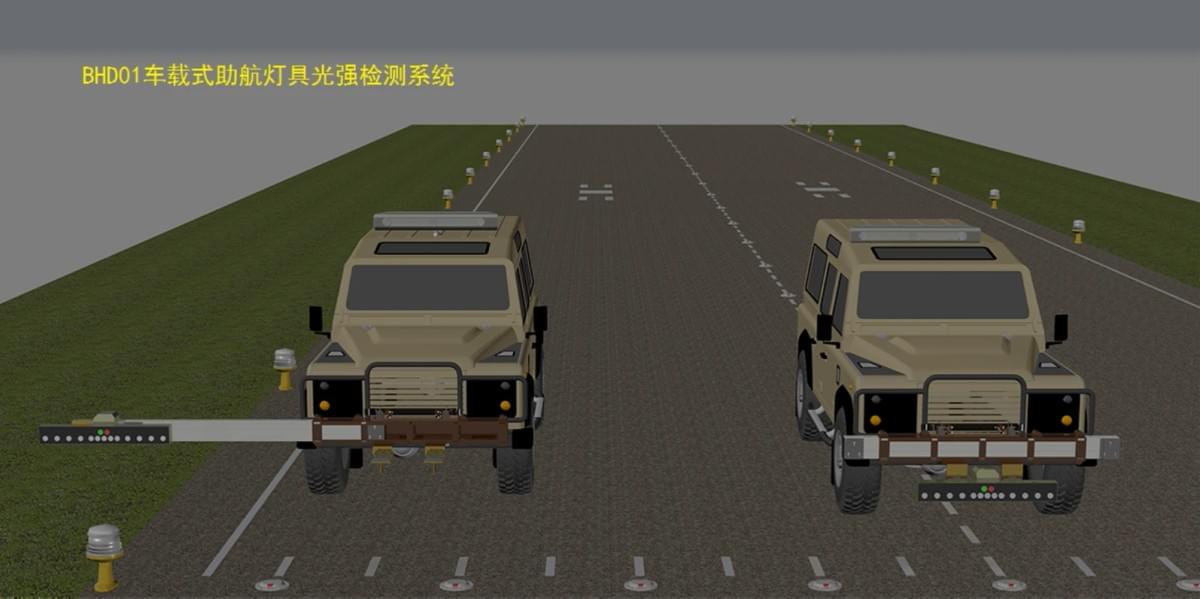
Even the most advanced runway lighting systems are only effective if they maintain the correct intensity levels. Over time, lights can dim due to wear and tear, weather damage, or electrical issues, which can compromise visibility and safety. To address this, airports need a reliable way to monitor light intensity in real time—and that’s where Haisen’s Light Intensity Tester comes in.
Why Real-Time Testing Matters
Traditional light intensity testing involves manual inspections, where technicians physically measure the brightness of each light using handheld devices. This process is time-consuming, labor-intensive, and prone to human error. It also only provides a snapshot of light performance at a specific moment, meaning issues that arise between inspections can go undetected until they impact flight operations.
Real-time online light intensity testing solves these problems by providing continuous monitoring of runway lights. Using advanced sensors and wireless technology, systems like Haisen’s Light Intensity Tester can measure the intensity of each light 24/7, transmitting data to a central dashboard where airport authorities can access it in real time. This allows for immediate detection of any lights that are not meeting ICAO intensity standards, enabling prompt maintenance or replacement.
The benefits of real-time testing are numerous:
- Enhanced Safety: By ensuring that all runway lights are operating at the correct intensity, real-time testing reduces the risk of accidents caused by poor visibility. Pilots can rely on consistent, bright lighting to guide them through takeoffs and landings, even in low-visibility conditions.
- Reduced Maintenance Costs: Real-time testing allows airports to address issues before they become major problems. For example, a dim light can be replaced before it burns out completely, avoiding the need for emergency repairs and reducing downtime.
- Improved Operational Efficiency: By eliminating the need for manual inspections, real-time testing saves airports time and labor costs. It also ensures that runway lighting systems are always in optimal condition, reducing the risk of flight delays caused by lighting malfunctions.
- Compliance with Standards: Real-time testing provides airports with accurate, up-to-date data on light intensity, making it easier to demonstrate compliance with ICAO regulations. This is critical for maintaining airport certification and avoiding penalties.
Haisen’s Light Intensity Tester: Setting the Industry Standard
Haisen’s Light Intensity Tester is a state-of-the-art solution that has revolutionized runway lighting maintenance. Designed specifically for airfield applications, this device offers a range of features that make it the preferred choice for airports worldwide:
- Real-Time Online Monitoring: The tester continuously measures light intensity and transmits data to a cloud-based platform, allowing airport authorities to monitor performance from anywhere, at any time.
- Precision Measurement: Using proprietary patented technology, Haisen’s tester provides accurate intensity readings within ±1% of the actual value, ensuring compliance with ICAO standards.
- Easy Integration: The system can be integrated with existing runway lighting systems, making retrofitting simple and cost-effective. It also works with both LED and traditional lighting technologies.
- Alerts and Notifications: When a light’s intensity falls below the required threshold, the system sends instant alerts to airport maintenance teams via email, SMS, or the central dashboard. This ensures that issues are addressed quickly, minimizing downtime.
- Data Analytics: Haisen’s tester collects historical data on light performance, allowing airports to identify trends and predict when lights may need replacement. This proactive approach helps airports plan maintenance schedules and budget effectively.
For example, a major international airport in Asia recently implemented Haisen’s Light Intensity Tester and saw a 60% reduction in lighting-related maintenance calls and a 25% improvement in compliance with ICAO intensity standards. The airport also reported fewer flight delays caused by lighting issues, leading to higher passenger satisfaction and operational efficiency.
The Future of Runway Lighting: Innovations on the Horizon
As aviation technology continues to advance, runway lighting is poised for further innovation. The future of runway lighting will focus on enhancing safety, improving efficiency, and integrating with other airfield systems to create a seamless, intelligent guidance network. Below are some of the key trends and innovations that will shape the future of runway lighting:
1. Smart Runway Lighting Systems
The next generation of runway lighting will be “smart,” meaning they can communicate with other airfield systems and adapt to changing conditions automatically. For example, smart runway lights could adjust their intensity based on real-time weather data (e.g., increasing brightness during heavy fog) or aircraft traffic (e.g., dimming when no aircraft are approaching). They could also integrate with aircraft navigation systems, providing pilots with personalized guidance based on their aircraft’s size, speed, and approach path.
Smart runway lighting systems will use the Internet of Things (IoT) technology to connect lights to a central network, enabling real-time data sharing and remote control. This will allow airports to optimize lighting performance, reduce energy consumption, and improve safety by ensuring that lights are always operating at the right intensity for the current conditions.
2. Solar-Powered Runway Lights
As airports strive to reduce their carbon footprint, solar-powered runway lights are becoming an increasingly popular option. These lights use solar panels to harness energy from the sun, storing it in batteries for use during nighttime or low-light conditions. Solar-powered lights are ideal for remote airports or areas with limited access to electrical grids, as they require no external power source.
Advancements in solar panel and battery technology have made solar-powered runway lights more efficient and reliable than ever before. Modern solar panels can generate enough energy to power lights even in cloudy weather, and high-capacity batteries can store energy for several days of use. Solar-powered lights also have a longer lifespan than traditional lights, as they have fewer moving parts and are less susceptible to electrical failures.
3. Enhanced Visibility with Adaptive Lighting
Adaptive lighting technology will allow runway lights to adjust their color and intensity based on the time of day, weather conditions, and aircraft type. For example, during daytime, lights could emit a dimmer, more energy-efficient light, while at night or during low visibility, they could switch to a brighter, more focused beam. Adaptive lighting could also use different colors to signal different conditions—e.g., amber lights to warn of wet runway surfaces or red lights to indicate a closed runway.
This technology will improve visibility for pilots while reducing energy consumption and light pollution. It will also help pilots make faster, more informed decisions by providing them with visual cues that are tailored to the current situation.
4. Integration with Autonomous Aircraft Systems
As autonomous aircraft (drones, self-flying planes) become more common, runway lighting will need to integrate with their navigation systems. Autonomous aircraft rely on sensors and cameras to navigate, and runway lighting will play a critical role in providing these systems with clear visual references. Future runway lights could be designed to emit specific frequencies or patterns that are easily detectable by autonomous aircraft sensors, ensuring that they can align with runways and taxiways accurately.
Integration with autonomous aircraft systems will also require runway lighting to be compatible with artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms, which will analyze lighting data to make real-time navigation decisions. This will help autonomous aircraft operate safely in all conditions, reducing the risk of accidents and improving the efficiency of air travel.

Choosing the Right Runway Lighting Solution for Your Airport
With so many runway lighting options available, choosing the right solution for your airport can be a daunting task. The key is to consider your airport’s specific needs, including traffic volume, operational requirements, weather conditions, and budget. Below are some factors to keep in mind when selecting a runway lighting system:
1. Operational Requirements
The first step is to determine your airport’s operational needs. Are you a small regional airport with primarily VFR operations, or a large commercial airport with high traffic volumes and IFR operations? Smaller airports may only require low-intensity runway lights, while larger airports will need high-intensity systems with advanced features like REILs, TDZLs, and centerline lights.
You should also consider the types of aircraft that use your airport. Large commercial aircraft require brighter, more concentrated lighting than small general aviation planes, so your runway lighting system should be tailored to the aircraft that will be operating there.
2. Weather Conditions
Weather conditions play a critical role in determining the type of runway lighting you need. If your airport is located in an area with frequent fog, rain, or snow, you’ll need high-intensity lights that are visible in low-visibility conditions. REILs and TDZLs are especially important for airports with challenging weather, as they provide pilots with clear visual cues during approach and landing.
You should also consider the temperature and humidity levels in your area. Lights that are resistant to extreme temperatures, moisture, and corrosion will be more reliable and require less maintenance.
3. Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
As airports face increasing pressure to reduce their environmental impact, energy efficiency and sustainability are important factors to consider. LED lights are the most energy-efficient option, consuming up to 80% less energy than traditional bulbs. Solar-powered lights are also a sustainable choice, as they reduce reliance on fossil fuels and lower carbon emissions.
When evaluating runway lighting solutions, look for products that have been certified for energy efficiency (e.g., ENERGY STAR) and that use eco-friendly materials. This will not only help you reduce your airport’s carbon footprint but also save money on energy and maintenance costs in the long run.
4. Maintenance and Reliability
Runway lighting systems should be reliable and easy to maintain. LED lights have a longer lifespan than traditional bulbs, reducing the need for frequent replacements. Real-time monitoring systems like Haisen’s Light Intensity Tester can also help you identify issues early, minimizing downtime and maintenance costs.
You should also consider the availability of spare parts and technical support. Choose a supplier that offers a comprehensive warranty and has a network of service technicians to provide support when needed. This will ensure that your runway lighting system remains operational and compliant with ICAO standards.
5. Cost
Cost is always a consideration when investing in runway lighting. While LED and smart lighting systems may have a higher upfront cost than traditional systems, they offer significant long-term savings in energy and maintenance. You should also consider the cost of installation, retrofitting (if applicable), and training for your staff.
To get the best value for your money, work with a supplier that can provide a customized solution tailored to your airport’s needs. They should be able to conduct a thorough assessment of your current lighting system and recommend upgrades that will improve safety and efficiency while staying within your budget.
Conclusion: Runway Lighting—The Foundation of Aviation Safety
Runway Lighting is more than just a series of lights on an airfield—it’s a critical safety system that guides pilots through the most dangerous phases of flight. From the earliest incandescent bulbs to today’s advanced LED systems and real-time monitoring tools, runway lighting has evolved to meet the demands of modern aviation, ensuring that flights are safe and efficient even in the most challenging conditions.
As technology continues to advance, the future of runway lighting looks brighter than ever. Innovations like smart lighting, solar power, adaptive lighting, and integration with autonomous aircraft systems will further enhance safety and efficiency, making air travel even more reliable for pilots and passengers alike.
For airports looking to upgrade their runway lighting systems, Haisen’s Light Intensity Tester and LED runway lighting solutions offer the perfect combination of performance, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. With real-time monitoring, precision measurement, and compliance with ICAO standards, Haisen’s products are designed to help airports maintain safe, efficient runway lighting systems that meet the needs of today’s aviation industry.
Investing in high-quality runway lighting is not just a legal requirement—it’s a commitment to safety, efficiency, and customer satisfaction. By choosing the right runway lighting solution, airports can ensure that they are well-equipped to handle the demands of modern air travel, now and in the future.

