In today’s tech-driven world, Drone Detection Radar stands as a cornerstone of airspace security, addressing the growing challenges posed by the widespread use of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). As drones become more accessible to consumers, businesses, and even malicious actors, the need for reliable, advanced Drone Detection Radar systems has never been more critical. These specialized radar solutions offer unparalleled capabilities to detect, track, classify, and respond to drone threats, ensuring the safety of critical infrastructure, public events, sensitive facilities, and national borders. From industrial complexes to airports, prisons to political rallies, Drone Detection Radar is redefining how we protect our airspace, privacy, and security in an era where UAVs are both a tool and a risk.
What Is Drone Detection Radar?
Drone Detection Radar is a cutting-edge surveillance technology engineered specifically to identify, monitor, and manage UAVs in diverse airspace environments. Unlike traditional radar systems that often overlook small, low-flying objects, Drone Detection Radar leverages advanced engineering and signal processing to focus on the unique characteristics of drones. At its core, this technology uses electromagnetic waves to scan the airspace, emitting radio signals that bounce off drones and other objects. By analyzing the reflected signals, Drone Detection Radar can extract critical data—including the drone’s location, altitude, speed, trajectory, and even size—providing real-time insights to security teams.
A key distinction of Drone Detection Radar is its ability to differentiate drones from other airborne objects such as birds, debris, or weather balloons. This is made possible through advanced techniques like micro-Doppler effect analysis, which detects the unique motion patterns of drone propellers, and frequency modulation, which enhances signal clarity. Modern Drone Detection Radar systems also integrate 3D technology, allowing for precise spatial tracking and minimizing false alarms—a common frustration with less sophisticated detection methods. Whether deployed in urban settings with heavy electromagnetic interference or remote areas with vast open spaces, Drone Detection Radar delivers consistent, accurate performance that security professionals can rely on.

How Does Drone Detection Radar Operate?
The operation of Drone Detection Radar is a sophisticated process that combines hardware innovation and software intelligence to deliver comprehensive UAV surveillance. Here’s a detailed breakdown of its key operational phases:
- Signal Emission: Drone Detection Radar systems emit high-frequency radio waves across a designated airspace. These waves are carefully calibrated to cover specific ranges and altitudes, depending on the application—from short-range coverage for event security to long-range scanning for border protection.
- Signal Reflection: When the emitted radio waves encounter a drone (or any object), they bounce back toward the radar system. Drones, with their metal components and distinct shapes, reflect signals in a pattern that is distinguishable from natural objects like birds or random debris.
- Signal Processing: The reflected signals are captured by the radar’s receivers and sent to a powerful signal processor. This processor uses advanced algorithms to filter out noise, analyze signal patterns, and extract actionable data. Techniques like micro-Doppler analysis play a crucial role here: by detecting the subtle frequency shifts caused by rotating drone propellers, the system can confirm that the object is a drone, not a bird or other non-threatening item.
- Classification and Tracking: Once a drone is detected, Drone Detection Radar classifies it based on factors such as size, speed, flight pattern, and radar cross-section (RCS). This classification helps security teams determine if the drone is a small consumer model, a commercial UAV, or a potentially threatening industrial-grade device. The system then tracks the drone in real time, updating its location and trajectory continuously to provide a complete picture of its movement.
- Alert Generation: When a drone enters a restricted airspace or exhibits suspicious behavior, the Drone Detection Radar triggers an alert. These alerts can be visual (on a monitoring screen), auditory (an alarm), or sent to connected devices (such as smartphones or security control panels), ensuring that security personnel are notified immediately.
Advanced Drone Detection Radar systems also offer multi-target tracking, allowing them to monitor multiple drones simultaneously without sacrificing accuracy. This is particularly valuable in high-traffic areas like airports or large events, where multiple UAVs may be present at once. Additionally, some systems integrate machine learning algorithms that improve over time, learning to recognize new drone models and adapt to emerging threats—ensuring long-term effectiveness in a rapidly evolving UAV landscape.
The Unmatched Advantages of Drone Detection Radar
Drone Detection Radar offers a range of benefits that set it apart from other UAV detection technologies, making it the preferred choice for security professionals across industries. Here are its most compelling advantages:
1. Wide Coverage Area
One of the primary strengths of Drone Detection Radar is its ability to cover large expanses of airspace with minimal hardware. Unlike optical cameras or acoustic detectors, which have limited range and require line-of-sight, Drone Detection Radar can monitor hundreds of acres with a single unit. For example, a single well-placed radar system can cover an entire industrial complex, a large agricultural field, or a section of a national border—reducing the need for multiple devices and lowering deployment costs. This wide coverage is especially valuable for organizations with extensive premises, as it ensures no blind spots and minimizes the manpower required for continuous surveillance.
2. All-Weather, 24/7 Operation
Adverse weather conditions—such as rain, fog, snow, or darkness—render many detection technologies ineffective. Optical cameras struggle in low light or poor visibility, while acoustic detectors can be overwhelmed by wind or ambient noise. Drone Detection Radar, however, operates independently of weather and lighting conditions. Electromagnetic waves penetrate fog, rain, and snow with ease, and the system works equally well day and night. This all-weather capability is critical for critical infrastructure protection, where security cannot be compromised by Mother Nature. For instance, an airport’s Drone Detection Radar will continue to detect unauthorized UAVs even during a heavy storm, ensuring that flights remain safe and operations are not disrupted.
3. High Detection Accuracy
Accuracy is non-negotiable in drone detection, and Drone Detection Radar delivers exceptional precision. By leveraging advanced signal processing and classification algorithms, these systems can distinguish drones from other airborne objects with remarkable reliability. This reduces false alarms—a major issue with traditional detection methods. For example, in a park or wildlife area with a high bird population, a conventional detector might trigger frequent false alerts. In contrast, Drone Detection Radar uses micro-Doppler analysis to identify the unique motion of drone propellers, filtering out bird movements and focusing only on genuine UAV threats. This high accuracy ensures that security teams do not waste time responding to false alarms and can focus on addressing real risks.
4. Real-Time Tracking and Instant Alerts
In security situations, every second counts. Drone Detection Radar provides real-time data on drone movements, allowing security teams to respond immediately to potential threats. As soon as a drone enters a restricted zone, the system detects it, classifies it, and triggers an alert—giving personnel ample time to assess the situation and take action. For example, if a drone is detected approaching a government building, security teams can mobilize quickly to intercept it, deploy countermeasures, or evacuate the area if necessary. This real-time capability is critical for preventing drone-related incidents, such as smuggling, espionage, or sabotage.
5. Minimal False Alarms
False alarms not only waste time and resources but also desensitize security teams to genuine threats. Drone Detection Radar addresses this issue through advanced technologies like machine learning and micro-Doppler analysis, which significantly reduce false alerts. By learning to recognize the unique characteristics of drones—such as their flight patterns, speed, and RCS—the system can accurately distinguish them from birds, balloons, or other debris. This means security teams can trust the alerts they receive, ensuring that they respond promptly to actual drone threats without being distracted by false notifications.
6. Versatility Across Environments
Drone Detection Radar is highly adaptable, performing effectively in a wide range of environments—from urban cities with tall buildings and electromagnetic interference to remote rural areas with open skies. In urban settings, high-frequency Drone Detection Radar can penetrate through clutter and identify small consumer drones flying between buildings. In remote areas, long-range Drone Detection Radar can monitor vast expanses, detecting drones from several kilometers away. This versatility makes it suitable for a diverse array of applications, from protecting skyscrapers in downtown areas to securing oil fields in remote regions.

Key Applications of Drone Detection Radar
Drone Detection Radar is used across numerous industries and sectors, where it plays a critical role in mitigating drone-related risks. Here are its most important applications:
1. Critical Infrastructure Protection
Critical infrastructure—including power plants, water treatment facilities, oil refineries, and telecommunications towers—is vital to public safety and economic stability. These facilities are increasingly targeted by malicious drones, which can be used to sabotage equipment, steal data, or cause environmental damage. Drone Detection Radar serves as a first line of defense, monitoring the airspace around these facilities 24/7. If an unauthorized drone is detected, the system alerts security teams, who can then deploy countermeasures—such as jamming devices or physical interceptors—to neutralize the threat. For example, a power plant’s Drone Detection Radar can detect a drone carrying explosives or hacking equipment, allowing security to intervene before any damage is done.
2. Airport Security
Airports are among the most sensitive areas for drone activity, as unauthorized UAVs pose a severe risk to aviation safety. A collision between a drone and an aircraft could result in catastrophic consequences, including loss of life. Drone Detection Radar is an integral part of airport security systems, monitoring the airspace around runways, terminals, and approach paths. The radar can detect drones at long distances, giving air traffic control and security teams time to respond. This may involve diverting flights, deploying counter-UAS systems to jam the drone’s signals, or alerting law enforcement to locate the operator. With Drone Detection Radar, airports can ensure that their airspace remains safe for commercial and private aircraft.
3. Homeland Security and Border Protection
Homeland security agencies rely on Drone Detection Radar to protect national borders, government buildings, embassies, and other sensitive sites. Drones are increasingly used for smuggling contraband (such as drugs, weapons, or explosives) across borders, as well as for espionage and terrorist activities. Drone Detection Radar systems deployed along borders can detect unauthorized UAVs from several kilometers away, allowing border patrol agents to intercept them before they cross into the country. In urban areas, Drone Detection Radar protects government buildings from drones that may be used to capture sensitive information or carry out attacks. This application is critical for maintaining national security and preventing threats to public safety.
4. Prison Security
Prisons face a growing threat from drones, which are used by external parties to smuggle drugs, weapons, cell phones, and other contraband to inmates. These items can fuel violence, enable criminal activity inside prisons, and compromise the safety of staff and prisoners. Drone Detection Radar deployed around prison perimeters can detect incoming UAVs, even at low altitudes or in areas with obstacles. Once a drone is detected, security personnel can track its flight path, determine its drop location, and intercept it before the contraband reaches inmates. Some prison systems integrate Drone Detection Radar with counter-UAS systems, which can jam the drone’s signals and force it to land, allowing authorities to seize the contraband and identify the operator.
5. Event Security
Large-scale events—such as sports games, music concerts, political rallies, and festivals—attract thousands of people, making them vulnerable to drone-related risks. Unauthorized drones can invade privacy, disrupt the event, or even pose a physical threat to attendees. Drone Detection Radar is used to monitor the airspace around event venues, detecting any UAVs that enter restricted areas. Security teams can then assess the drone’s intent: if it’s a recreational user flying in a no-fly zone, they can ask the operator to land the drone; if it’s a potential threat, they can deploy countermeasures to neutralize it. Drone Detection Radar ensures that events remain safe and secure for attendees, performers, and staff.
6. Commercial and Industrial Site Security
Commercial and industrial sites—such as warehouses, manufacturing facilities, construction sites, and agricultural fields—also benefit from Drone Detection Radar. Drones can be used to steal intellectual property (by photographing sensitive equipment or processes), vandalize property, or disrupt operations. Drone Detection Radar monitors the airspace around these sites, detecting unauthorized UAVs and alerting security teams. For example, a construction company can use Drone Detection Radar to protect a high-value project from drones that may be used to spy on designs or cause delays. Agricultural operations can use the technology to prevent drones from interfering with crop dusting or stealing proprietary farming data.

Types of Drone Detection Radars
Drone Detection Radar systems come in various types, each designed to meet specific application requirements. The choice of radar depends on factors such as coverage range, portability, frequency, and environment. Here are the most common types:
1. High-Frequency Radars
High-frequency Drone Detection Radars operate at frequencies above 10 GHz (such as Ku-band, Ka-band, or X-band), offering high resolution and the ability to detect small drones with precision. These radars are ideal for environments where accuracy is paramount, such as urban areas, airports, and critical infrastructure sites. High-frequency radars can distinguish between small consumer drones (like DJI Mavic models) and other small objects, reducing false alarms. They also perform well in areas with electromagnetic interference, as their high frequency allows them to cut through clutter. For example, in a city with tall buildings and numerous electronic devices, a high-frequency Drone Detection Radar can accurately track drones flying between structures, ensuring no threats go undetected.
2. Long-Range Radars
Long-range Drone Detection Radars are designed to detect UAVs at distances of up to 10 kilometers or more. These radars are typically used for border security, large industrial sites, and military applications, where early detection is critical. Long-range radars use lower frequencies (such as L-band or S-band) to achieve extended coverage, as lower frequencies travel farther and penetrate obstacles more effectively. For example, a long-range Drone Detection Radar deployed along a national border can detect drones approaching from several kilometers away, giving border patrol agents ample time to prepare a response. In large industrial sites like oil refineries or mining operations, long-range radars provide comprehensive coverage of vast areas, ensuring that no unauthorized drones enter the premises.
3. Portable Radars
Portable Drone Detection Radars are lightweight, compact, and easy to transport, making them suitable for mobile security operations and temporary events. These radars can be set up in minutes and deployed in remote locations or areas where permanent installation is not feasible. Portable radars are often used by law enforcement, military units, and event security teams. For example, a police department can use a portable Drone Detection Radar to monitor a temporary protest or demonstration. A concert promoter can deploy portable radars around a festival venue to ensure airspace security for a single event. Portable radars typically have a shorter range than long-range systems but offer flexibility and ease of use.
4. Ground-Based vs. Airborne Radars
Most Drone Detection Radars are ground-based, installed on fixed structures (like poles, buildings, or trailers) or mounted on vehicles (such as trucks or SUVs) for mobile surveillance. Ground-based radars are ideal for stationary applications, such as protecting a facility or border. Airborne Drone Detection Radars, on the other hand, are mounted on aircraft (like helicopters, drones, or planes) to provide aerial surveillance. These radars are used for large-scale monitoring, such as searching for drones in remote areas or tracking UAVs over wide regions. Airborne Drone Detection Radars offer a bird’s-eye view of the airspace, making them suitable for military operations or search-and-rescue missions.

Integration with Other Systems for Enhanced Security
Drone Detection Radar is most effective when integrated with other security systems, creating a comprehensive UAV defense ecosystem. By combining radar data with data from other sensors and countermeasures, organizations can achieve greater situational awareness and a faster response to threats. Here are the key integration opportunities:
1. Multi-Sensor Integration
Integrating Drone Detection Radar with other sensors—such as infrared (IR) cameras, acoustic detectors, and radio frequency (RF) sensors—enhances detection accuracy and provides a more complete picture of drone activity. Each sensor contributes unique capabilities:
- Infrared Cameras: IR cameras capture thermal images of drones, even in low light or poor visibility. When integrated with Drone Detection Radar, IR cameras provide visual confirmation of detected drones, allowing security teams to identify the UAV’s model, size, and operator (if visible).
- Acoustic Detectors: Acoustic detectors pick up the sound of drone motors, providing an additional layer of detection—especially in areas where radar signals may be blocked (such as dense forests or urban canyons). When combined with radar, acoustic detectors can confirm the presence of a drone and help locate it.
- RF Sensors: RF sensors detect the radio frequency signals emitted by drone control systems. This helps identify the drone’s operator, as RF sensors can track the source of the control signals. Integrating RF sensors with Drone Detection Radar allows security teams to not only detect the drone but also locate and apprehend the operator.
Multi-sensor integration creates a “sensor fusion” system, where data from all sources is combined and analyzed to eliminate blind spots and reduce false alarms. For example, if a Drone Detection Radar detects a potential UAV, the IR camera can confirm it’s a drone (not a bird), the acoustic detector can verify the sound of its motors, and the RF sensor can track the operator’s location. This comprehensive approach ensures that no drone threat goes undetected or unaddressed.
2. Integration with Counter-UAS Systems
Drone Detection Radar is often paired with counter-unmanned aerial system (C-UAS) technologies to create a complete “detect and defeat” solution. Once a drone is detected and classified by the radar, the system automatically shares data with the C-UAS platform, which can then deploy appropriate countermeasures. Common C-UAS technologies include:
- Jamming Systems: These devices disrupt the drone’s communication and control signals, causing it to lose connectivity with the operator. The drone may then land automatically, return to its starting point, or hover in place—allowing security teams to intercept it.
- Physical Interceptors: These include drone-catching nets, laser systems, or other physical devices that disable or capture the drone. For example, a net-carrying drone can be deployed to intercept an unauthorized UAV, wrapping it in a net and bringing it to the ground.
- GPS Spoofing: This technology sends fake GPS signals to the drone, tricking it into flying to a safe location (such as a designated landing zone) where it can be seized.
Integration with C-UAS systems ensures a swift response to drone threats. For example, if a Drone Detection Radar at an airport detects an unauthorized UAV in the flight path, the system can immediately send data to a jamming device, which disrupts the drone’s signals and forces it to land safely—preventing a potential collision with an aircraft. This seamless integration of detection and countermeasures is critical for high-security environments where even a small delay could have catastrophic consequences.
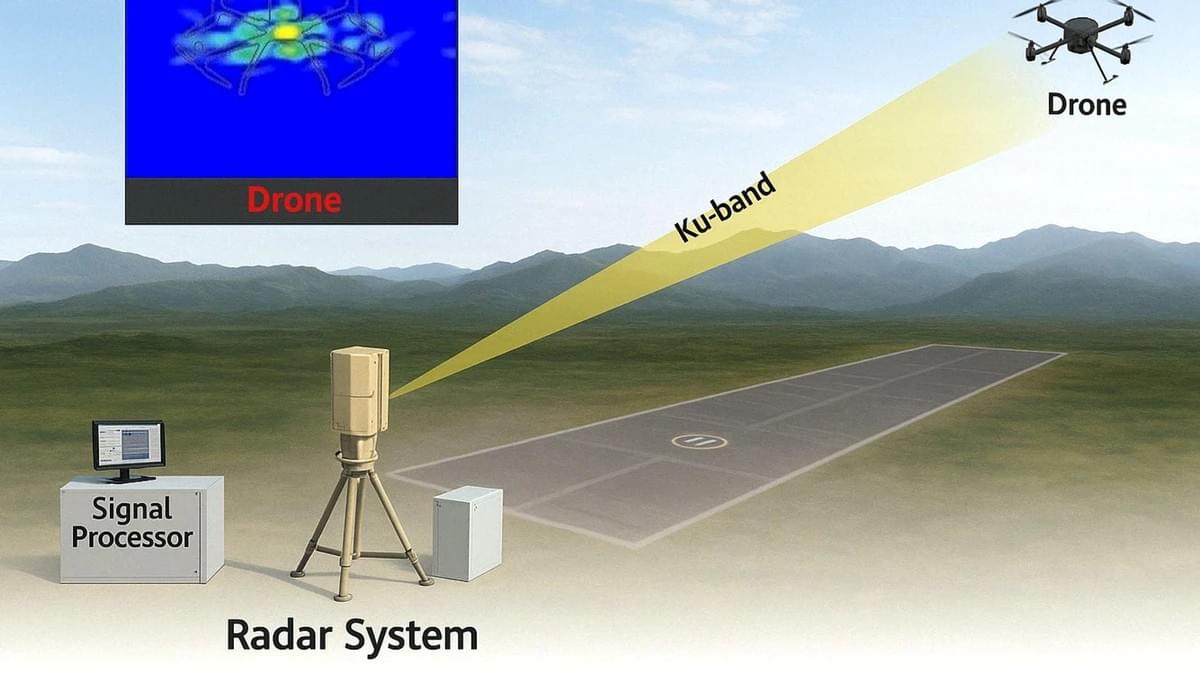
Future Trends in Drone Detection Radar Technology
As drone technology evolves, so too does Drone Detection Radar. Innovations in artificial intelligence, miniaturization, and signal processing are driving the next generation of UAV surveillance systems. Here are the key trends to watch:
1. Advancements in AI and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are transforming Drone Detection Radar, making systems smarter, more accurate, and more adaptable. AI-powered algorithms can analyze radar data in real time, identifying patterns and anomalies that human operators might miss. For example, ML models can learn to recognize the unique flight patterns of different drone models, allowing the radar to classify UAVs with greater precision. AI also enables predictive analytics, where the system can anticipate potential drone threats based on historical data—such as identifying areas where drones are frequently detected and deploying additional security measures.
Another key application of AI is adaptive learning. As new drone models with advanced anti-detection features (such as stealth coatings or low-RCS designs) emerge, AI-enabled Drone Detection Radar can analyze their unique characteristics and update its detection algorithms—ensuring that it remains effective against evolving threats. This continuous learning capability is critical in a market where drone technology is advancing rapidly.
2. Miniaturization and Cost-Effectiveness
Drone Detection Radar systems are becoming smaller, lighter, and more affordable, making them accessible to a broader range of users. Miniaturization is driven by advancements in component technology, such as smaller antennas, more efficient signal processors, and low-power microchips. These compact radars can be deployed in a wider range of applications—including on-board vehicles (such as police cars or boats), small businesses, and even wearable devices for individual security.
Cost reduction is another key trend. As manufacturing processes improve and component costs decrease, Drone Detection Radar is no longer limited to large organizations with significant budgets. Small-to-medium-sized businesses, local governments, and even individual security professionals can now afford to deploy drone detection technology. This increased accessibility will drive adoption across sectors, making airspace security more widespread.
3. Enhanced Detection Capabilities
Future Drone Detection Radar systems will offer even greater detection capabilities, including the ability to detect smaller, stealthier drones. New radar technologies—such as millimeter-wave (mmWave) radars and quantum-enhanced radars—are being developed to address the challenges posed by low-RCS drones. MmWave radars operate at frequencies between 30 GHz and 300 GHz, offering ultra-high resolution and the ability to detect even tiny drones (such as micro-UAVs) with precision. Quantum-enhanced radars use quantum computing principles to improve signal sensitivity, allowing them to detect drones that are currently undetectable by traditional radar systems.
Additionally, future Drone Detection Radar will be able to operate in more challenging environments, such as areas with strong electromagnetic interference or complex urban landscapes. Advanced signal processing techniques will enable radars to filter out noise and clutter, ensuring accurate detection even in the most demanding conditions.
4. Increased Connectivity and Cloud Integration
Drone Detection Radar systems are moving toward greater connectivity, with cloud-based platforms that allow for remote monitoring and data sharing. Cloud integration enables security teams to access radar data from anywhere in the world, using smartphones, tablets, or computers. This is particularly valuable for organizations with multiple locations, as it allows for centralized monitoring of all Drone Detection Radar systems. Cloud platforms also facilitate data analytics, where large volumes of radar data can be analyzed to identify trends, optimize deployment, and improve overall security.
Another aspect of connectivity is the integration of Drone Detection Radar with Internet of Things (IoT) devices. For example, radar systems can be connected to smart cameras, access control systems, and alarm systems, creating a fully integrated security ecosystem. If a drone is detected, the system can automatically lock doors, activate cameras, and alert security personnel—streamlining the response process.

Why Choose Drone Detection Radar for Your Security Needs?
In a world where drones are becoming increasingly prevalent, Drone Detection Radar is not just a luxury—it’s a necessity. Whether you’re protecting critical infrastructure, securing an airport, or ensuring the safety of a large event, Drone Detection Radar offers the reliability, accuracy, and versatility needed to mitigate drone-related risks. Here’s why you should invest in this technology:
- Proactive Threat Mitigation: Drone Detection Radar provides early warning of potential threats, allowing you to respond before a drone can cause damage, steal data, or compromise security.
- 24/7, All-Weather Protection: Unlike other detection technologies, Drone Detection Radar operates around the clock, regardless of weather conditions—ensuring continuous security.
- Reduced False Alarms: Advanced algorithms and signal processing minimize false alerts, saving time and resources for your security team.
- Scalability: Drone Detection Radar systems can be scaled to meet your specific needs, whether you’re protecting a small business or a large national border.
- Future-Proof Technology: With ongoing advancements in AI, miniaturization, and detection capabilities, Drone Detection Radar will continue to evolve and adapt to new threats—ensuring long-term value for your investment.
Conclusion
Drone Detection Radar is a critical technology for safeguarding airspace, security, and privacy in an era of widespread drone use. Its ability to detect, track, classify, and respond to UAV threats—combined with its wide coverage, all-weather operation, and high accuracy—makes it the preferred choice for security professionals across industries. From critical infrastructure and airports to prisons and events, Drone Detection Radar plays a vital role in mitigating drone-related risks and ensuring public safety.
As technology advances, Drone Detection Radar will become even more powerful, with AI-driven capabilities, miniaturized designs, and enhanced detection features. By integrating with other sensors and counter-UAS systems, it will create comprehensive security ecosystems that provide complete protection against evolving drone threats.
If you’re looking to enhance your security posture and protect your assets from drone-related risks, Drone Detection Radar is the solution. Invest in this cutting-edge technology today and ensure that your airspace remains safe, secure, and protected—now and in the future.
Contact us today to learn more about our Drone Detection Radar solutions and how they can be tailored to your specific security needs. Our team of experts is ready to help you design a comprehensive UAV surveillance system that delivers peace of mind and unmatched protection.

