Airfield Ground Lighting (AGL) is the cornerstone of safe and efficient modern airport operations, delivering critical visual guidance for aircraft takeoff, landing, and taxiing in all visibility conditions. From low-intensity setups for small regional airports to high-intensity smart systems powering major international hubs, AGL systems are engineered to align with global aviation standards and adapt to the evolving needs of the aviation industry, making them an irreplaceable part of aerodrome infrastructure worldwide.
In the fast-paced world of aviation, where every second counts and safety is non-negotiable, airports rely on Airfield Ground Lighting to eliminate operational risks, streamline aircraft movement, and ensure compliance with international regulatory frameworks set by the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO), Federal Aviation Administration (FAA), and European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA). Without a robust Airfield Ground Lighting system, even the most advanced airports would struggle to operate after dark or in adverse weather—such as fog, heavy rain, or snow—leading to costly delays, reduced capacity, and heightened safety hazards for aircraft, crew, passengers, and ground personnel. This comprehensive guide explores the technical fundamentals, core components, key features, global standards, real-world applications, and future innovations of Airfield Ground Lighting, while highlighting how investing in modern AGL systems drives long-term value for airport operators across the Americas, Middle East, East Asia, and beyond.
What Is an Airfield Ground Lighting (AGL) System?
At its core, an Airfield Ground Lighting system is a specialized network of light fixtures, power distribution equipment, and control systems designed to provide targeted illumination and visual signaling for all ground and near-ground aircraft operations. Unlike general outdoor lighting, Airfield Ground Lighting is built to meet the strict performance requirements of aviation, with lights calibrated for long-distance visibility, color-coded signaling, and reliable operation in extreme environmental conditions. Every element of an AGL system—from the bulbs and lenses to the control panels and monitoring tools—works in tandem to guide pilots through every phase of airport navigation: from the initial approach to touchdown, taxiing to the apron, and parking at designated stands.
Airfield Ground Lighting systems are not one-size-fits-all; they are tailored to an airport’s operational scale, traffic volume, and geographic location. A small regional airport operating under Visual Flight Rules (VFR) may only require a basic Low-Intensity Lighting System (LILS) for runway and taxiway guidance, while a major international hub handling thousands of flights daily needs a fully automated High-Intensity Lighting System (HILS) that supports Category III landings in zero-visibility conditions. Regardless of the scale, the primary objective of any Airfield Ground Lighting system remains the same: to create a clear, intuitive visual path for aircraft and reduce the risk of human error, runway incursions, and ground collisions—all of which are critical to maintaining seamless airport operations.

Technical Principles Powering Airfield Ground Lighting Systems
The functionality of Airfield Ground Lighting systems is rooted in a seamless integration of electrical and optical engineering, with every design choice optimized for aviation-specific performance. At the heart of any AGL system is a dedicated power distribution network that delivers a stable, uninterrupted electricity supply—an absolute necessity, as even a momentary power failure can disrupt airport operations and compromise safety. This network feeds a network of light fixtures strategically placed along runways, taxiways, aprons, and obstacle structures, with each fixture engineered to emit light in specific patterns, intensities, and colors to convey actionable information to pilots.
Airfield Ground Lighting systems use three primary types of light sources, each with distinct advantages for aviation applications: incandescent, halogen, and light-emitting diode (LED) bulbs. Incandescent and halogen bulbs were the traditional choice for decades, offering high brightness but suffering from high energy consumption, short lifespans, and frequent maintenance needs. In recent years, LED airfield lights have become the gold standard for Airfield Ground Lighting, thanks to their superior energy efficiency (using up to 80% less power than traditional bulbs), extended lifespans (often exceeding 50,000 hours), low heat output, and durability in extreme temperatures—all critical benefits for airports in the Middle East’s arid climates, East Asia’s humid regions, and the Americas’ diverse weather zones.
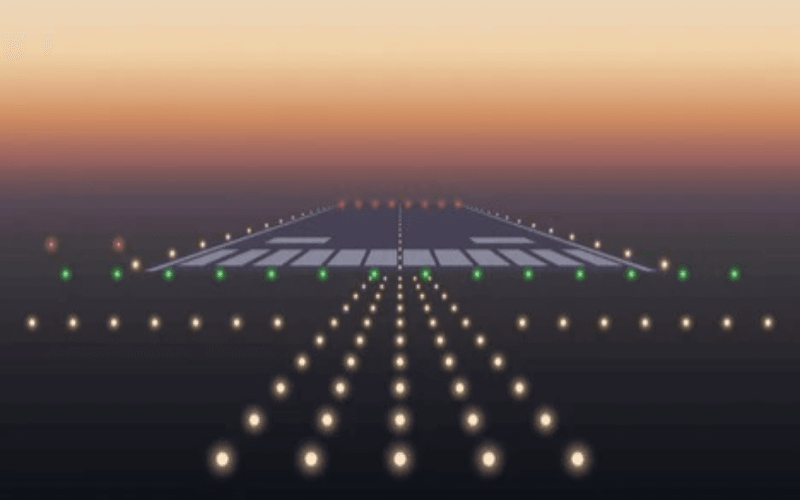
Optical components such as precision lenses and reflectors are equally vital to Airfield Ground Lighting performance, shaping and directing light to create distinct visual cues for pilots. For example, runway edge lights use narrow-beam lenses to project a bright white light horizontally along the runway’s perimeter, ensuring visibility from several miles away. Touchdown zone lights use wide-beam lenses to illuminate the runway’s landing area, while approach lighting systems (ALS) use a combination of flashing and steady lights to guide pilots from instrument flight to visual flight during the final landing phase. These optical design choices ensure that Airfield Ground Lighting signals are clear and unambiguous, even in low-visibility conditions where pilot visibility is limited to a few hundred feet.
Complementing the lighting fixtures themselves are advanced control and monitoring systems that form the "brain" of modern Airfield Ground Lighting. These systems include light management equipment, control processing units, and real-time monitoring tools that integrate with air traffic control (ATC) radar, surface movement radar, and MLAT/ADS-B technology. This integration allows airport operators to adjust lighting intensity remotely, monitor fixture performance in real time, and trigger automated alerts for faulty lights—ensuring that Airfield Ground Lighting systems remain fully operational at all times. For runway safety, the Runway Status Lighting System (RWSL), a key subcomponent of Airfield Ground Lighting, uses takeoff holding lights (THL) and runway entry lights (REL) to prevent runway incursions by monitoring aircraft and vehicle movements in real time, a critical feature for high-traffic airports.
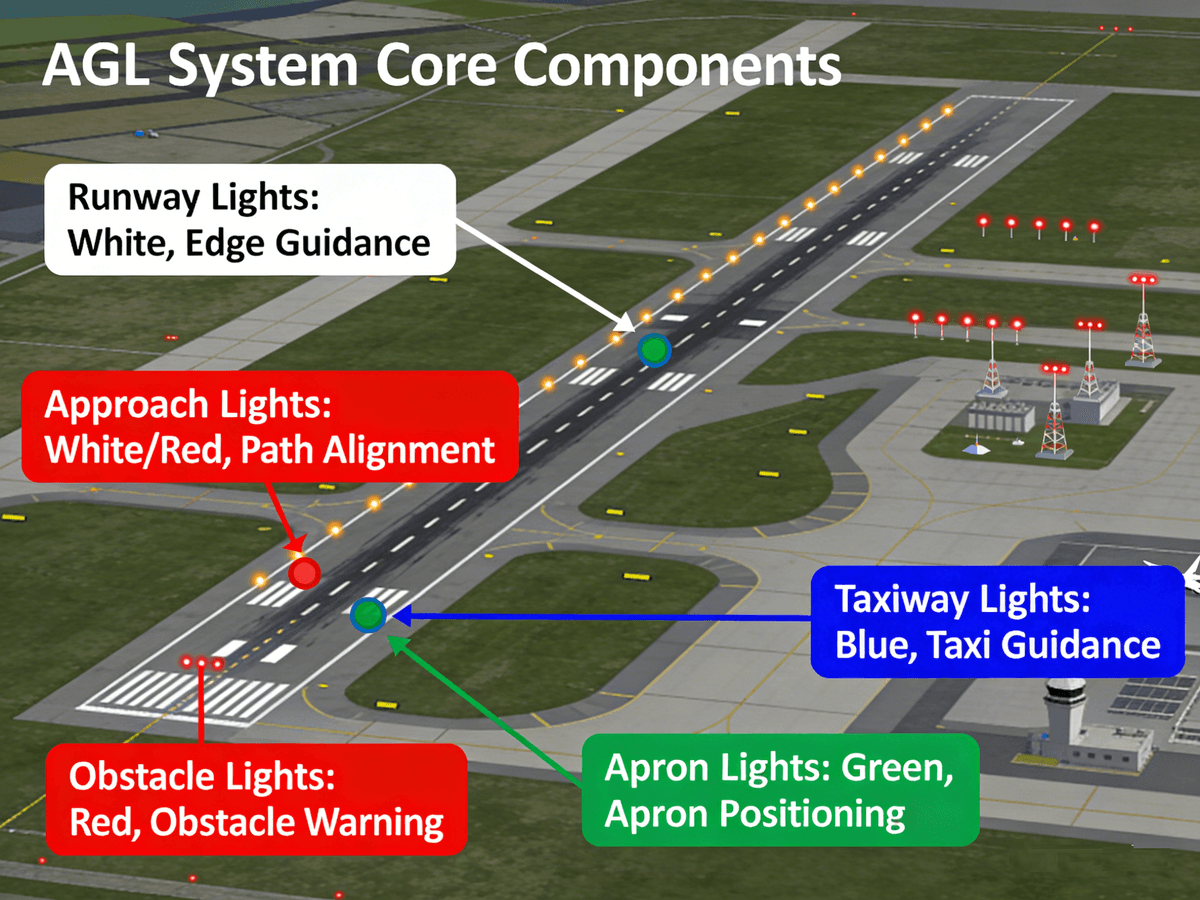
Core Components of a Comprehensive Airfield Ground Lighting System
A fully functional Airfield Ground Lighting system is composed of interrelated subsystems, each designed to address a specific aspect of airport navigation and safety. Every component is calibrated to meet global Airfield Ground Lighting standards, with color-coding, spacing, and intensity strictly defined by ICAO Annex 14, FAA AC 150/5345-26F, and EASA certification requirements. Below is a detailed breakdown of the essential components of modern Airfield Ground Lighting, all of which work together to create a complete visual guidance system for airports:
Runway Lighting
Runway lighting is the most critical component of Airfield Ground Lighting, as it defines the airport’s most vital operational zone and guides aircraft during takeoff and landing. This subsystem includes:
- Runway Edge Lights: White lights installed at regular intervals along the runway’s edges to define its width and boundaries, a staple of all Airfield Ground Lighting systems.
- Runway Centerline Lights: Embedded in the runway surface, these alternating white and red lights (red near the runway end) guide pilots to maintain perfect alignment during takeoff and landing.
- Runway Threshold Lights: Green lights marking the start of the landing runway (red for the opposite end) that signal the beginning of the usable runway surface.
- Touchdown Zone Lights (TDZL): High-intensity white lights that illuminate the runway’s designated landing area, providing critical visual cues for pilots to judge touchdown point.
- Runway End Identifier Lights (REIL): Flashing white lights positioned on either side of the runway threshold, designed to help pilots identify the runway in low-visibility or low-light conditions.
All runway lighting components are color-coded and spaced according to Airfield Ground Lighting standards, with intensity adjustable to match ambient light and weather conditions—from bright daylight to zero-visibility fog.
Approach Lighting Systems (ALS)
Approach Lighting Systems are a specialized subcomponent of Airfield Ground Lighting that bridges the gap between instrument flight and visual flight for landing aircraft, making them essential for Instrument Flight Rules (IFR) operations and Category II/III landings. Common ALS types integrated into Airfield Ground Lighting systems include:
- ALSF-II: Advanced Lighting System with Sequenced Flashing Lights, the most sophisticated ALS for Category III landings, featuring a series of flashing lights that guide pilots along the approach path to the runway.
- SSALR: Short Approach Lighting System with Runway Alignment Indicator Lights, a compact ALS for medium-sized airports, providing basic approach guidance with runway alignment cues.
- ODALS: Omnidirectional Approach Lighting System, a low-cost ALS for small airports, delivering 360-degree visibility for approach guidance.
ALS is often paired with Precision Approach Path Indicators (PAPI)—a key part of Airfield Ground Lighting approach guidance—that use red and white lights to help pilots maintain the correct glide path for landing, ensuring they do not approach too high or too low.
Taxiway Lighting
Taxiway lighting is the backbone of ground navigation in Airfield Ground Lighting systems, guiding aircraft safely from the runway to the apron and vice versa, and preventing collisions with other aircraft or ground vehicles. This subsystem includes:
- Taxiway Edge Lights: Steady blue lights that define the lateral boundaries of taxiways, a universal Airfield Ground Lighting standard for taxiway identification.
- Taxiway Centerline Lights: Green lights embedded in the taxiway surface that guide pilots along the correct taxi route, with flashing green lights marking rapid exit taxiways for quick runway clearance.
- Holding Position Lights: Red lights that mark the runway hold line, signaling pilots to stop and wait for ATC clearance before entering the runway— a critical feature for preventing runway incursions.
- Runway Guard Lights: Flashing red and white lights positioned at taxiway-runway intersections, an additional safety layer in Airfield Ground Lighting that alerts pilots to the adjacent runway.
Apron and Ramp Lighting
Apron and ramp lighting is a vital part of Airfield Ground Lighting that illuminates aircraft parking areas, cargo loading zones, maintenance facilities, and passenger boarding gates. This subsystem uses high-intensity floodlights and LED-based Airfield Ground Lighting fixtures to provide uniform illumination, ensuring safe ground operations for aircraft, ground crew, and service vehicles. Apron lighting also includes illuminated position markers and gate number signs, all integrated into the overall Airfield Ground Lighting system, to guide pilots to designated parking stands and help ground personnel perform their duties safely after dark or in low visibility.
Obstruction Lighting
Obstruction lighting is a safety-critical subcomponent of Airfield Ground Lighting that warns pilots of potential hazards around the airport perimeter and within the airfield boundary. Installed on tall structures such as control towers, wind turbines, buildings, and antennas, these lights are designed to be highly visible day and night, with color and intensity defined by Airfield Ground Lighting standards: low-intensity red lights for short structures, and high-intensity white flashing lights for tall structures (over 45 meters). Obstruction lighting is a mandatory part of all Airfield Ground Lighting systems, as it prevents aircraft collisions with fixed structures in the airport’s airspace.
Global Airfield Ground Lighting Standards and Regulatory Compliance
For Airfield Ground Lighting systems to be effective and interoperable across the globe, strict adherence to international standards is non-negotiable. Airports in the Americas, Middle East, East Asia, and every other region must design, install, and maintain their Airfield Ground Lighting systems to meet the specifications set by three key regulatory bodies, whose guidelines form the foundation of all modern Airfield Ground Lighting design:
- ICAO Annex 14 - Aerodromes: The International Civil Aviation Organization’s Annex 14 is the global benchmark for Airfield Ground Lighting, outlining minimum requirements for light intensity, color, spacing, placement, and performance for all aerodrome lighting systems. ICAO Annex 14 ensures that Airfield Ground Lighting systems are consistent across all international airports, allowing pilots to navigate unfamiliar airports with confidence— a critical factor for global aviation travel.
- FAA AC 150/5345-26F: The U.S. Federal Aviation Administration’s technical specification sets detailed standards for Airfield Ground Lighting fixtures, including LED airfield lights, incandescent bulbs, and optical components. FAA standards are widely adopted in the Americas and serve as a reference for Airfield Ground Lighting design in many other regions, with a focus on durability, performance, and energy efficiency.
- EASA Certification Requirements: The European Union Aviation Safety Agency governs Airfield Ground Lighting system certification and installation practices for European airports, with strict guidelines for system integration, automation, and safety. EASA standards are increasingly adopted in the Middle East and East Asia, particularly for airports with high volumes of European air traffic.
Compliance with these Airfield Ground Lighting standards is not just a regulatory requirement—it is a critical factor in maintaining an airport’s operational license, attracting international airlines, and ensuring the safety of passengers and crew. Non-compliant Airfield Ground Lighting systems can lead to fines, flight restrictions, and a loss of reputation for airports, making regulatory adherence a top priority for airport operators worldwide. Additionally, regular maintenance and testing of Airfield Ground Lighting systems are required to maintain compliance, with airport operators mandated to conduct daily inspections of critical lighting components and annual full-system audits.
Key Features of Modern Airfield Ground Lighting Systems
Today’s Airfield Ground Lighting systems are far more than just a network of lights—they are advanced, smart infrastructure designed to deliver maximum safety, efficiency, and sustainability for airports. The latest Airfield Ground Lighting technology incorporates a range of features that address the evolving needs of the aviation industry, from energy conservation to real-time automation, making them a strategic investment for airport operators. Below are the defining features of modern Airfield Ground Lighting systems, all of which contribute to their value and performance:
High-Intensity Illumination for All Visibility Conditions
The primary feature of Airfield Ground Lighting is its ability to deliver high-intensity, long-distance illumination that remains visible in the most challenging conditions—including night, fog, rain, snow, and haze. High-intensity Airfield Ground Lighting fixtures are engineered to emit light with a high candela rating, ensuring that runway and taxiway signals are clear to pilots from several miles away. For example, high-intensity runway edge lights can be seen from over 10 miles away in clear weather, and from several hundred feet in zero-visibility fog— a critical feature for Category III landings. This high-intensity illumination is non-negotiable for Airfield Ground Lighting, as it forms the basis of all pilot visual guidance.
Standardized Color-Coded Signaling
Airfield Ground Lighting systems use a universal color-coding system that is recognized by pilots worldwide, a feature defined by ICAO and FAA Airfield Ground Lighting standards. This system ensures that visual signals are unambiguous and easy to interpret, even for pilots navigating an airport for the first time:
- White: Runway edges, centerlines, touchdown zones, and REIL—signaling active runway surfaces for takeoff and landing.
- Green: Runway thresholds, taxiway centerlines, and safe approach paths—signaling clear and usable areas for aircraft movement.
- Red: Runway ends, holding position lines, closed taxiways, and obstacles—signaling hazards or restricted areas to avoid.
- Blue: Taxiway edges—signaling the boundary of taxiway surfaces, a unique color for taxiway identification in Airfield Ground Lighting.
- Yellow: Apron marking lights and taxiway shoulder lights—signaling non-critical ground areas for parking and maintenance.
This color-coded signaling is a cornerstone of Airfield Ground Lighting safety, as it allows pilots to make split-second decisions based on clear visual cues, reducing the risk of human error.
Adjustable and Dynamic Lighting Levels
Modern Airfield Ground Lighting systems feature adjustable lighting intensity, a game-changing feature that optimizes visibility and energy efficiency. Airport operators can control Airfield Ground Lighting levels remotely, adjusting brightness based on ambient light (day vs. night), weather conditions (clear vs. fog), and traffic volume (peak vs. off-peak). For example, Airfield Ground Lighting intensity can be reduced to 20% during bright daylight to save energy, and increased to 100% during night or fog to ensure maximum visibility. Advanced Airfield Ground Lighting systems even offer dynamic real-time adjustment, with sensors that detect ambient light and weather conditions and automatically optimize lighting levels—eliminating the need for manual control and ensuring optimal performance at all times.
Energy-Efficient LED Technology
LED technology has revolutionized Airfield Ground Lighting, becoming the preferred light source for airports worldwide due to its unmatched energy efficiency, durability, and low maintenance needs. LED airfield lights use up to 80% less electricity than traditional incandescent and halogen bulbs, reducing airport energy bills significantly— a critical savings for high-traffic airports with extensive Airfield Ground Lighting systems. LED airfield lights also have a lifespan of over 50,000 hours, compared to just 1,000 hours for incandescent bulbs, meaning fewer replacements and lower maintenance costs for Airfield Ground Lighting. Additionally, LED airfield lights produce minimal heat, reducing the risk of fire hazards and extending the life of lighting fixtures— a key benefit for airports in hot climates such as the Middle East and the American Southwest. For sustainability-focused airports, LED Airfield Ground Lighting is a foundational element of reducing carbon footprints and meeting green aviation goals.
Compatibility with Aviation Navigation Aids
Airfield Ground Lighting systems are designed to integrate seamlessly with other critical aviation navigation aids, creating a comprehensive guidance system for pilots. This compatibility is a key feature of modern Airfield Ground Lighting, as it ensures that visual and electronic guidance work in tandem to enhance safety and accuracy. Airfield Ground Lighting integrates with:
- Instrument Landing System (ILS): A precision navigation system that guides aircraft during approach, with Airfield Ground Lighting aligned to the ILS glide path for a continuous visual-electronic approach.
- Visual Approach Slope Indicator (VASI) and PAPI: Slope guidance systems that use colored lights to help pilots maintain the correct landing glide path, integrated with Airfield Ground Lighting approach systems.
- Satellite Navigation Systems (GPS/GLONASS): Modern Airfield Ground Lighting systems can sync with satellite-based navigation, allowing for precise alignment of runway and taxiway lights with satellite-defined approach paths.
- ATC and Surface Movement Radar: Airfield Ground Lighting control systems integrate with ATC radar to monitor aircraft and vehicle movements, triggering automated lighting adjustments and runway safety alerts (e.g., RWSL).
This seamless integration makes Airfield Ground Lighting a central part of the airport’s overall navigation ecosystem, enhancing the accuracy and safety of all aircraft operations.
Remote Monitoring and Automated Maintenance Alerts
Modern Airfield Ground Lighting systems include advanced remote monitoring and diagnostic tools that allow airport operators to track fixture performance in real time. These tools send automated alerts to maintenance teams when a light fixture fails or malfunctions, ensuring that Airfield Ground Lighting issues are resolved quickly—often before they impact airport operations. For large airports with extensive Airfield Ground Lighting networks, this remote monitoring feature eliminates the need for manual inspections of every light fixture, reducing maintenance labor costs and improving system reliability. Some advanced Airfield Ground Lighting systems even use AI-powered predictive maintenance, analyzing fixture performance data to identify potential issues before they occur— a cutting-edge feature for smart airports.
Unmatched Benefits of Investing in a Modern Airfield Ground Lighting System
For airport operators, investing in a state-of-the-art Airfield Ground Lighting system is not just a capital expenditure—it is a strategic investment that delivers tangible, long-term benefits across safety, operational efficiency, cost savings, and regulatory compliance. Airfield Ground Lighting is the backbone of airport operations, and a modern, well-maintained system transforms how an airport functions, even in the most challenging conditions. Below are the key benefits that Airfield Ground Lighting brings to airports of all sizes, from small regional hubs to major international gateways:
Enhanced Aviation Safety: The Top Priority
The most significant benefit of Airfield Ground Lighting is its ability to drastically improve aviation safety by eliminating key operational risks. A well-designed Airfield Ground Lighting system provides clear visual guidance for pilots in all visibility conditions, reducing the risk of runway incursions, ground collisions, and landing errors— the leading causes of airport-related aviation accidents. The Runway Status Lighting System (RWSL), a key part of modern Airfield Ground Lighting, prevents runway incursions by monitoring aircraft and vehicle movements in real time, a feature that has been proven to reduce incursion risks by over 70% in high-traffic airports. The color-coded signaling of Airfield Ground Lighting also ensures that pilots are aware of hazards and restricted areas, allowing them to take immediate action to avoid danger. Studies by the FAA and ICAO have consistently shown that airports with modern Airfield Ground Lighting systems have significantly lower accident and incident rates than those with outdated or non-compliant systems, making Airfield Ground Lighting the single most important investment an airport can make for safety.
Airfield Ground Lighting also enhances safety for ground personnel, providing uniform illumination for apron and ramp operations, cargo loading, and aircraft maintenance. This illumination ensures that ground crew can perform their duties safely after dark or in low visibility, reducing the risk of workplace accidents and improving overall ground operation safety. For passengers, Airfield Ground Lighting translates to peace of mind, knowing that the airport has the infrastructure to ensure their safe arrival and departure— a key factor in building passenger trust and loyalty.
Improved Operational Efficiency and Airport Capacity
A modern Airfield Ground Lighting system streamlines aircraft movement, reducing ground delays and increasing overall airport capacity. With clear, reliable Airfield Ground Lighting guidance, pilots can taxi, take off, and land more quickly and smoothly, reducing the time aircraft spend on the ground. For example, rapid exit taxiway lights— a part of Airfield Ground Lighting taxiway systems— guide aircraft to exit the runway quickly after landing, allowing the next aircraft to land or take off in less time. This faster aircraft turnaround time increases the airport’s hourly flight capacity, a critical benefit for high-traffic airports facing congestion. Airfield Ground Lighting also reduces the risk of flight delays caused by low visibility, as a high-intensity system supports Category II/III landings in zero-visibility conditions— ensuring that flights can operate on schedule even when weather is poor. For airports in regions with frequent fog or low visibility (e.g., London Heathrow, Dubai International), Airfield Ground Lighting is the key to maintaining uninterrupted operations and avoiding costly weather-related delays.
The adjustable lighting levels of modern Airfield Ground Lighting also optimize operational efficiency by matching lighting performance to traffic volume. During off-peak hours, Airfield Ground Lighting intensity can be reduced to save energy, while during peak hours, it is increased to support the high volume of aircraft movements. This flexibility ensures that the airport’s resources are used efficiently, without compromising safety or performance.
Substantial Long-Term Cost Savings
While the initial investment in a modern Airfield Ground Lighting system may be significant, it delivers substantial long-term cost savings for airport operators, offsetting the upfront cost over time. The single biggest cost-saving feature of modern Airfield Ground Lighting is LED technology, which reduces energy consumption by up to 80% compared to traditional incandescent and halogen bulbs. For a major international airport, this translates to millions of dollars in annual electricity savings— a massive reduction in operational costs. LED airfield lights also have a much longer lifespan, meaning fewer bulb replacements and lower maintenance labor costs for Airfield Ground Lighting systems. A single LED airfield light can last over 50,000 hours, while an incandescent bulb needs replacement every 1,000 hours— eliminating the need for frequent, costly maintenance checks and replacements.
Airfield Ground Lighting also reduces costs by avoiding costly operational disruptions. A single runway incursion or weather-related delay can cost an airport hundreds of thousands of dollars in aircraft damage, passenger compensation, and lost revenue. A modern Airfield Ground Lighting system prevents these disruptions, ensuring that the airport operates smoothly and avoids these unnecessary costs. Additionally, Airfield Ground Lighting compliance with international standards eliminates the risk of regulatory fines and flight restrictions, which can be financially devastating for airports. For airports that upgrade to solar-powered Airfield Ground Lighting systems (e.g., Nairobi Jomo Kenyatta International Airport), the cost savings are even greater, with zero electricity costs for the lighting system and a drastically reduced carbon footprint.
Regulatory Compliance and Global Aviation Access
Compliance with international Airfield Ground Lighting standards is a mandatory requirement for all airports that wish to operate international flights. A modern Airfield Ground Lighting system ensures that an airport meets the guidelines set by ICAO, FAA, and EASA, allowing it to maintain its operational license, attract international airlines, and connect to the global aviation network. For airports in the Middle East and East Asia—fast-growing aviation hubs—Airfield Ground Lighting compliance is critical to competing in the global aviation market, as international airlines only operate to airports that meet the highest safety and operational standards. A compliant Airfield Ground Lighting system also makes it easier for airports to obtain Category II/III landing certification, a key credential for airports that want to operate in low-visibility conditions and attract more international flights.
Sustainability and Reduced Carbon Footprint
Modern Airfield Ground Lighting systems are a key part of airport sustainability initiatives, helping operators reduce their carbon footprint and meet global green aviation goals. LED airfield lights use far less energy than traditional bulbs, reducing the airport’s electricity consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. Many airports are now pairing LED Airfield Ground Lighting with renewable energy sources such as solar power, creating a fully sustainable lighting system with zero carbon emissions. For example, Nairobi Jomo Kenyatta International Airport’s solar-powered Airfield Ground Lighting system has reduced the airport’s carbon footprint by over 30% for ground lighting operations, a significant achievement for African aviation. Airfield Ground Lighting systems also reduce light pollution, with precision optical design that directs light only where it is needed— avoiding unnecessary light spillage into surrounding communities and natural areas. This sustainability focus not only benefits the environment but also enhances the airport’s reputation as a responsible corporate citizen, a key factor for attracting eco-conscious passengers and airlines.
Real-World Airfield Ground Lighting Success Stories
Airports across the globe have upgraded their Airfield Ground Lighting systems to modern LED and smart technology, reaping the benefits of improved safety, efficiency, and cost savings. These real-world case studies demonstrate the transformative impact of Airfield Ground Lighting on airport operations, and serve as a blueprint for other airport operators looking to invest in AGL upgrades:
Dubai International Airport (DXB) – Middle East’s Smart AGL Leader
Dubai International Airport, one of the world’s busiest international hubs, has implemented a state-of-the-art Airfield Ground Lighting system featuring LED technology and intelligent control systems. The airport’s Airfield Ground Lighting system is fully automated, with real-time remote monitoring and dynamic lighting adjustment, supporting Category III landings in the region’s frequent fog and sandstorms. The LED Airfield Ground Lighting upgrade has reduced the airport’s energy consumption by over 75% for ground lighting operations, saving millions of dollars in annual electricity costs, while also improving visibility for pilots and reducing maintenance needs. Dubai’s Airfield Ground Lighting system is integrated with the airport’s smart ATC and navigation systems, making it a model for modern Airfield Ground Lighting in the Middle East.
London Heathrow Airport (LHR) – Category III HILS for Zero-Visibility Operations
London Heathrow, Europe’s busiest airport, relies on a High-Intensity Lighting System (HILS) as its core Airfield Ground Lighting infrastructure, designed to support Category III landings in zero-visibility fog— a common weather condition in the UK. Heathrow’s Airfield Ground Lighting system is fully integrated with ILS and ATC radar, ensuring seamless coordination between visual and electronic guidance for pilots. The system’s Runway Status Lighting (RWSL) has drastically reduced runway incursion risks, even with the airport’s high flight volume (over 1,200 flights daily). Heathrow’s investment in Airfield Ground Lighting has allowed the airport to maintain uninterrupted operations in the most challenging visibility conditions, making it one of the most reliable international hubs in Europe.
Nairobi Jomo Kenyatta International Airport (NBO) – Solar-Powered AGL for Sustainability
Nairobi Jomo Kenyatta International Airport, a key aviation hub in Africa, recently upgraded to a solar-powered Airfield Ground Lighting system, a first for the region. The system uses LED airfield lights paired with solar panels and battery storage, eliminating electricity costs for ground lighting operations and reducing the airport’s carbon footprint by over 30%. The wireless design of the solar Airfield Ground Lighting system allowed for rapid installation with minimal disruption to airport operations, a key benefit for a busy regional hub. The upgrade has also improved visibility for pilots in Nairobi’s low-visibility rainy seasons, enhancing safety and reducing flight delays. Nairobi’s solar Airfield Ground Lighting system is a model for sustainable aviation infrastructure in developing regions, proving that AGL can be both cost-effective and eco-friendly.
Future Trends Shaping the Evolution of Airfield Ground Lighting
The aviation industry is constantly evolving, and Airfield Ground Lighting technology is no exception. As airports become smarter, more sustainable, and more connected, Airfield Ground Lighting systems are set to undergo significant innovation, with new technologies and design approaches that further enhance safety, efficiency, and sustainability. Below are the key future trends that will shape the next generation of Airfield Ground Lighting systems, driving the evolution of airport infrastructure for years to come:
AI-Powered Smart Airfield Lighting Systems
The future of Airfield Ground Lighting is smart, with AI and machine learning at the core of next-generation systems. AI-powered Airfield Ground Lighting will use advanced sensors to detect real-time conditions—including aircraft position, weather, ambient light, and traffic volume—and automatically optimize lighting levels, patterns, and intensity for maximum safety and efficiency. These smart Airfield Ground Lighting systems will also use predictive analytics to identify potential maintenance issues before they occur, reducing downtime and improving system reliability. AI will also enable Airfield Ground Lighting to integrate with other smart airport systems (e.g., autonomous ground vehicles, digital ATC) to create a fully connected airport ecosystem, where every component works in tandem to streamline operations. For example, AI-powered Airfield Ground Lighting can adjust lighting in real time to guide autonomous aircraft and ground vehicles, a key feature for the future of autonomous aviation.
Deeper Integration with Advanced Navigation Technologies
Airfield Ground Lighting systems will increasingly integrate with the next generation of aviation navigation technologies, moving beyond traditional ILS and VASI to satellite-based and digital navigation systems. This integration will include precise synchronization with GPS, GLONASS, and Galileo satellite systems, allowing Airfield Ground Lighting to align with satellite-defined approach paths and runway boundaries for unmatched accuracy. Airfield Ground Lighting will also integrate with digital flight guidance systems, such as Required Navigation Performance (RNP) and Area Navigation (RNAV), creating a seamless visual-electronic guidance system for pilots. For airports, this deeper integration means more precise aircraft navigation, reduced reliance on traditional ground-based navigation aids, and improved safety for all flight operations.
Sustainable and Renewable Energy-Powered AGL
Sustainability will remain a driving force for Airfield Ground Lighting innovation, with airports increasingly adopting renewable energy sources to power their lighting systems. Solar power will become more widespread for Airfield Ground Lighting, with advanced solar panels and battery storage technology making off-grid lighting systems a viable option for airports of all sizes. Wind power and geothermal energy will also be integrated into Airfield Ground Lighting power systems for airports in suitable regions, further reducing carbon emissions. Additionally, Airfield Ground Lighting manufacturers will focus on creating more eco-friendly fixtures, using recycled materials and eliminating hazardous substances in production— making AGL systems sustainable from design to disposal. Light pollution reduction will also be a key focus, with Airfield Ground Lighting fixtures designed to direct light only where it is needed, minimizing impact on surrounding ecosystems and communities.
Ultra-Durable and Low-Maintenance AGL Fixtures
Future Airfield Ground Lighting fixtures will be engineered for even greater durability and low maintenance, with materials that can withstand the harshest environmental conditions—from extreme heat and cold to saltwater corrosion (for coastal airports) and sandstorms (for desert airports). LED airfield lights will continue to evolve, with even longer lifespans (exceeding 100,000 hours) and higher energy efficiency, while also becoming more affordable for small and medium-sized airports. Self-cleaning and self-repairing AGL fixtures will also emerge, using advanced coatings to prevent dust and dirt buildup (a key issue for Middle Eastern airports) and small robotic components to repair minor malfunctions— eliminating the need for manual maintenance and reducing costs even further.
Modular and Scalable AGL Systems
Future Airfield Ground Lighting systems will be designed to be modular and scalable, allowing airport operators to expand or upgrade their systems with minimal disruption to operations. Modular Airfield Ground Lighting components will be easy to install and replace, with plug-and-play design that eliminates the need for extensive wiring and construction. This scalability is critical for fast-growing airports in the Middle East, East Asia, and the Americas, which need to expand their AGL systems to match increasing flight volume. Modular Airfield Ground Lighting also makes it easier for small airports to upgrade to more advanced systems as their operations grow, without the need for a full system replacement.
Why Your Airport Needs a Modern Airfield Ground Lighting Upgrade
Airfield Ground Lighting is not just a part of airport infrastructure—it is the lifeline of safe, efficient, and compliant airport operations. For airport operators, an outdated, non-compliant, or inefficient Airfield Ground Lighting system is a significant risk, leading to safety hazards, operational delays, high costs, and lost revenue. In contrast, a modern, state-of-the-art Airfield Ground Lighting system transforms your airport, delivering enhanced safety, increased capacity, substantial cost savings, and regulatory compliance—all while positioning your airport for the future of smart, sustainable aviation.
Whether you operate a small regional airport in the Americas, a busy hub in the Middle East, or a growing gateway in East Asia, investing in Airfield Ground Lighting is a strategic decision that delivers long-term value for your business, your passengers, and your community. LED Airfield Ground Lighting, smart control systems, and renewable energy integration are no longer luxury features—they are essential for competing in the global aviation market and meeting the evolving demands of pilots, airlines, and passengers.
If you are ready to upgrade your airport’s Airfield Ground Lighting system, or to install a new system that aligns with global standards and future trends, partnering with a trusted AGL technology provider is critical. The right provider will design a custom Airfield Ground Lighting system tailored to your airport’s unique needs, ensuring optimal performance, safety, and efficiency for years to come. With the right Airfield Ground Lighting system, your airport can operate seamlessly in all conditions, reduce its environmental impact, and build a reputation as a safe, reliable, and forward-thinking aviation hub.
Call to Action
Elevate your airport’s safety, efficiency, and sustainability with a custom Airfield Ground Lighting system designed to meet global ICAO/FAA/EASA standards and your unique operational needs. Our team of aviation lighting experts specializes in LED Airfield Ground Lighting, smart control systems, and solar-powered AGL solutions for airports across the Americas, Middle East, and East Asia. Contact us today for a free consultation and discover how our cutting-edge Airfield Ground Lighting technology can transform your airport operations and deliver long-term value.rAirfield Ground Lighting: The Light of Modern Airportsound Lighting: The Light of Modern Airports

