The Aviation Cabin Heating Machine is a critical piece of equipment designed to maintain comfortable and safe temperatures inside aircraft cabins when planes are on the ground, with their engines shut down. Without the Aviation Cabin Heating Machine, passengers and crew could face uncomfortable or even dangerous cold conditions during ground stops, especially in regions with harsh winter climates or during cold seasons.
Aircraft spend a significant amount of time on the ground between flights, undergoing boarding, deboarding, refueling, maintenance, and other operations. During these ground stops, the aircraft's engines are typically turned off to conserve fuel and reduce emissions. However, this means that the aircraft's internal heating systems, which rely on engine power, are also inactive. The Aviation Cabin Heating Machine steps in to fill this gap, providing a reliable source of warm air to keep the cabin at a comfortable temperature, ensuring passenger satisfaction and safety, and protecting sensitive equipment from cold-related damage. In this comprehensive blog post, we will explore the various aspects of the Aviation Cabin Heating Machine, including its functionality, types, key features, benefits, maintenance requirements, and future trends.
The Importance of Aviation Cabin Heating Machine in Aircraft Operations
The Aviation Cabin Heating Machine plays a vital role in ensuring the smooth and safe operation of aircraft, particularly during ground stops. Here are some key reasons why this equipment is essential:
- Passenger Comfort: Maintaining a comfortable cabin temperature is crucial for passenger satisfaction. Cold cabins during ground stops can lead to discomfort, complaints, and a negative overall travel experience. The Aviation Cabin Heating Machine ensures that the cabin remains warm, even in freezing external temperatures, making the waiting time on the ground more pleasant for passengers.
- Passenger Safety: Extreme cold in the cabin can pose health risks to passengers, especially children, the elderly, and those with health conditions. Prolonged exposure to cold can cause hypothermia, frostbite, or exacerbate existing medical issues. The Aviation Cabin Heating Machine helps prevent these risks by keeping the cabin at a safe and warm temperature.
- Crew Comfort and Performance: Flight crew and cabin crew also need a comfortable working environment to perform their duties effectively. Cold conditions can distract crew members, reduce their focus, and even affect their physical performance. The Aviation Cabin Heating Machine ensures that the crew can work in a comfortable setting, contributing to overall operational safety.
- Protection of Aircraft Equipment: Aircraft cabins are equipped with various sensitive electronic equipment, such as avionics, communication systems, and lighting. Extreme cold can damage these components, leading to malfunctions and costly repairs. The Aviation Cabin Heating Machine helps maintain a stable temperature, protecting the equipment from cold-related damage.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many aviation regulatory bodies, such as the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) and the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA), have standards and guidelines regarding passenger comfort and safety, which include maintaining appropriate cabin temperatures during ground stops. The Aviation Cabin Heating Machine helps airlines comply with these regulations, avoiding potential fines and penalties.
- Operational Efficiency: Cold cabins can lead to delays during boarding and deboarding, as passengers may be reluctant to enter or exit a cold aircraft. By keeping the cabin warm, the Aviation Cabin Heating Machine helps ensure that these processes run smoothly, reducing turnaround times and improving operational efficiency.

How Aviation Cabin Heating Machine Works
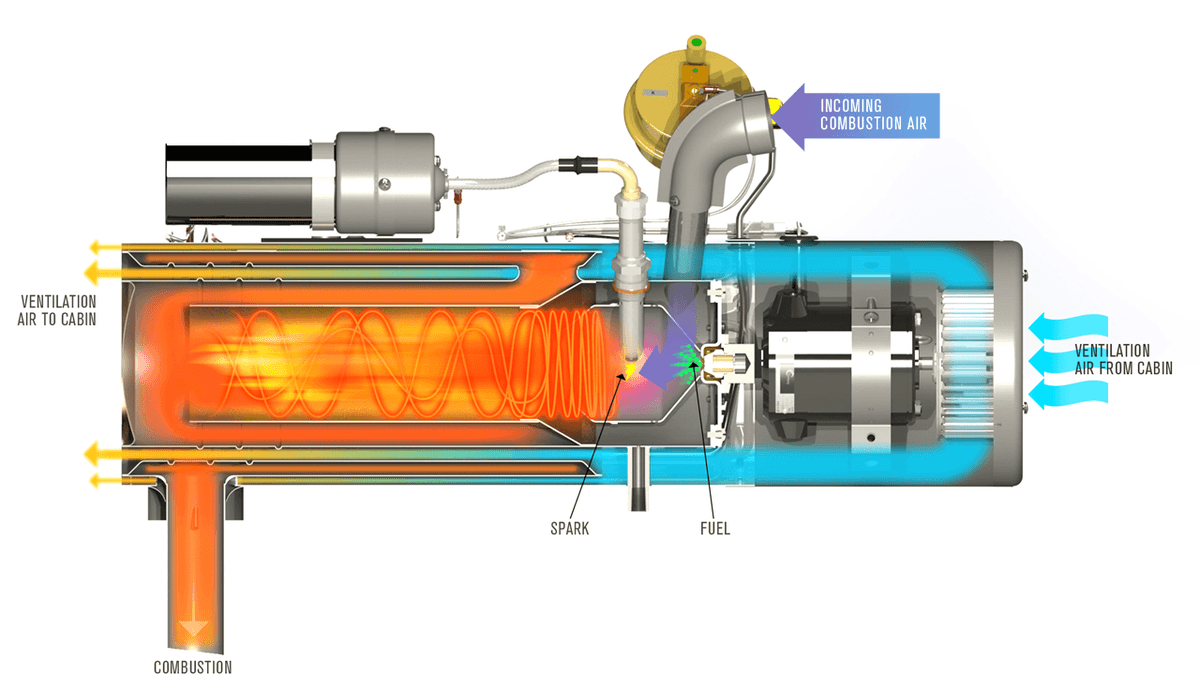
The Aviation Cabin Heating Machine operates by generating and delivering warm air into the aircraft cabin. The basic working principle involves several key steps, which may vary slightly depending on the type and model of the machine. Here is a general overview of how the Aviation Cabin Heating Machine works:
- Air Intake: The machine draws in ambient air from the surrounding environment through an intake system. This air may be cold, especially in winter conditions, but it is the starting point for the heating process.
- Heating Element: The intake air is passed through a heating element, which is typically powered by diesel, gasoline, electricity, or a combination of these. The heating element raises the temperature of the air to the desired level, which is usually between 20°C and 25°C (68°F and 77°F), depending on the aircraft's requirements and external conditions.
- Air Circulation: Once the air is heated, it is circulated through a system of ducts and hoses that connect the Aviation Cabin Heating Machine to the aircraft's cabin. The warm air is distributed evenly throughout the cabin, ensuring that all areas receive sufficient heat.
- Temperature Control: Most Aviation Cabin Heating Machines are equipped with temperature control systems that allow operators to set and maintain the desired cabin temperature. These systems may include thermostats, sensors, and feedback mechanisms that adjust the heating output based on the current cabin temperature, ensuring a stable and comfortable environment.
- Exhaust Management: For fuel-powered Aviation Cabin Heating Machines, the combustion process produces exhaust gases, which must be safely vented away from the aircraft and passengers. The machine is designed with an exhaust system that directs these gases away from the cabin and ground crew, preventing the risk of carbon monoxide exposure.
- Safety Features: The Aviation Cabin Heating Machine is equipped with various safety features to ensure safe operation. These may include overheat protection, which shuts off the machine if the temperature exceeds a safe level; flame sensors, which detect and extinguish flames in case of a malfunction; and pressure relief valves, which prevent excessive pressure buildup in the system.
Types of Aviation Cabin Heating Machines
There are several types of Aviation Cabin Heating Machines available, each designed to meet specific needs and operating conditions. The main types are categorized based on their power source:
- Diesel-Powered Aviation Cabin Heating Machine: This is one of the most common types of Aviation Cabin Heating Machines. It uses diesel fuel to power the heating element, which generates heat through combustion. Diesel-powered machines are known for their high heating capacity and durability, making them suitable for use in cold climates and for large aircraft. They are also relatively fuel-efficient, making them a cost-effective option for extended ground stops. However, they produce exhaust emissions, which require proper ventilation.
- Gasoline-Powered Aviation Cabin Heating Machine: Similar to diesel-powered machines, gasoline-powered Aviation Cabin Heating Machines use gasoline as a fuel source. They are generally lighter and more portable than diesel-powered models, making them suitable for smaller aircraft and operations where mobility is important. However, gasoline is more flammable than diesel, requiring extra safety precautions during storage and use. They also tend to have higher fuel consumption than diesel-powered machines.
- Electric-Powered Aviation Cabin Heating Machine: Electric-powered Aviation Cabin Heating Machines use electricity to power the heating element, which is typically a resistance heater. They are emission-free, making them environmentally friendly and suitable for use in enclosed spaces or areas with strict emission regulations. They are also quieter than fuel-powered machines, reducing noise pollution around the airport. However, they require a reliable source of electricity, which may be a challenge in remote locations or during power outages. They also have a lower heating capacity compared to fuel-powered machines, making them more suitable for smaller aircraft or milder climates.
- Hybrid Aviation Cabin Heating Machine: Hybrid models combine two or more power sources, such as diesel and electricity, to provide greater flexibility and efficiency. For example, a hybrid machine may use electricity for heating in areas where power is available and switch to diesel in remote locations. This allows operators to choose the most suitable power source based on the operating conditions, reducing fuel consumption and emissions when possible.
- Portable Aviation Cabin Heating Machine: Portable models are designed for easy transportation and use with multiple aircraft. They are typically smaller and lighter than stationary models, with wheels or handles for mobility. Portable Aviation Cabin Heating Machines are ideal for airlines with a diverse fleet of aircraft or for use in temporary or remote locations. They may be powered by gasoline, diesel, or electricity, depending on the model.
- Stationary Aviation Cabin Heating Machine: Stationary models are permanently installed at specific locations on the airport tarmac, such as gate positions or maintenance areas. They are connected to a fixed power source, such as a diesel generator or the airport's electrical grid, and are designed to service aircraft parked at that location. Stationary machines are typically larger and more powerful than portable models, making them suitable for large aircraft and high-volume operations.
Key Features of a High-Quality Aviation Cabin Heating Machine
When selecting an Aviation Cabin Heating Machine, it is important to consider its key features to ensure that it meets the specific needs of the operation. Here are some essential features of a high-quality Aviation Cabin Heating Machine:
- High Heating Capacity: The machine should be able to generate sufficient heat to warm the cabin of the target aircraft, even in extreme cold conditions. Heating capacity is typically measured in British Thermal Units (BTUs) per hour or kilowatts (kW). A higher heating capacity is necessary for larger aircraft or colder climates.
- Efficient Fuel Consumption: For fuel-powered machines, efficient fuel consumption is important to reduce operating costs and minimize emissions. The machine should be designed to maximize heat output while minimizing fuel usage, ensuring that it can operate for extended periods without refueling.
- Temperature Control Precision: The machine should have accurate and reliable temperature control systems to maintain the desired cabin temperature within a narrow range. This helps ensure passenger comfort and protects aircraft equipment from temperature fluctuations.
- Quick Heating Response: The machine should be able to reach the desired operating temperature quickly, reducing the time it takes to warm the cabin. This is particularly important for short ground stops, where every minute counts.
- Even Air Distribution: The machine should be able to distribute warm air evenly throughout the cabin, ensuring that all areas, including seating, galleys, and lavatories, receive sufficient heat. This may involve a well-designed duct system and adjustable vents.
- Durable Construction: The Aviation Cabin Heating Machine operates in harsh airport environments, exposed to extreme temperatures, wind, rain, snow, and vibration. It should be constructed with durable materials, such as stainless steel or heavy-duty plastic, to withstand these conditions and ensure long-term reliability.
- Safety Features: As mentioned earlier, the machine should be equipped with a range of safety features, including overheat protection, flame sensors, exhaust gas monitoring, and pressure relief valves. These features help prevent accidents and ensure the safety of passengers, crew, and ground personnel.
- Easy Maintenance: The machine should be designed for easy maintenance, with accessible components and clear maintenance instructions. This helps reduce downtime and ensures that the machine remains in good working order. Features such as removable filters, easy-to-access heating elements, and diagnostic systems can simplify maintenance tasks.
- Compatibility with Aircraft: The Aviation Cabin Heating Machine should be compatible with the aircraft types it will service. This includes having the correct hose connections, duct sizes, and heating capacity to match the aircraft's cabin requirements. Manufacturers often provide compatibility charts to help operators select the right machine for their fleet.
- Noise Reduction: Noise pollution is a concern in airport environments, so the machine should be designed to operate as quietly as possible. This is particularly important for machines used near passenger terminals or residential areas. Noise levels are typically measured in decibels (dB), and a lower dB rating indicates a quieter machine.
Benefits of Using Aviation Cabin Heating Machine
The use of Aviation Cabin Heating Machine offers numerous benefits for airlines, airports, passengers, and crew. Here are some of the key benefits:
- Enhanced Passenger Experience: By keeping the cabin warm during ground stops, the Aviation Cabin Heating Machine significantly improves the passenger experience. Passengers are more likely to have a positive perception of the airline if they are comfortable during all stages of their journey, including waiting on the ground. This can lead to increased customer loyalty and repeat business.
- Improved Safety: The machine helps maintain a safe environment for passengers and crew by preventing cold-related health issues and protecting aircraft equipment from damage. This contributes to overall aviation safety and reduces the risk of accidents or incidents caused by cold-related factors.
- Reduced Operational Costs: While there is an initial investment in purchasing an Aviation Cabin Heating Machine, the long-term operational costs are often lower than the costs associated with cold-related delays, equipment damage, and passenger compensation. Efficient fuel consumption and low maintenance requirements further reduce operational costs.
- Compliance with Regulations: As mentioned earlier, the Aviation Cabin Heating Machine helps airlines comply with regulatory standards regarding passenger comfort and safety. This avoids potential fines and penalties, which can be costly for airlines.
- Increased Operational Efficiency: Warm cabins facilitate faster boarding and deboarding processes, reducing turnaround times. This allows airlines to maintain their flight schedules more effectively, improving on-time performance and increasing the number of flights that can be operated in a day.
- Environmental Benefits: Electric-powered and hybrid Aviation Cabin Heating Machines produce fewer emissions than traditional fuel-powered models, contributing to a reduction in the airport's carbon footprint. This aligns with the aviation industry's goal of reducing environmental impact and meeting sustainability targets.
- Flexibility and Versatility: The availability of different types of Aviation Cabin Heating Machines, including portable and stationary models, provides airlines and airports with flexibility to choose the right equipment for their specific needs. This versatility allows them to adapt to changing operating conditions, such as different aircraft types, weather conditions, and operational requirements.
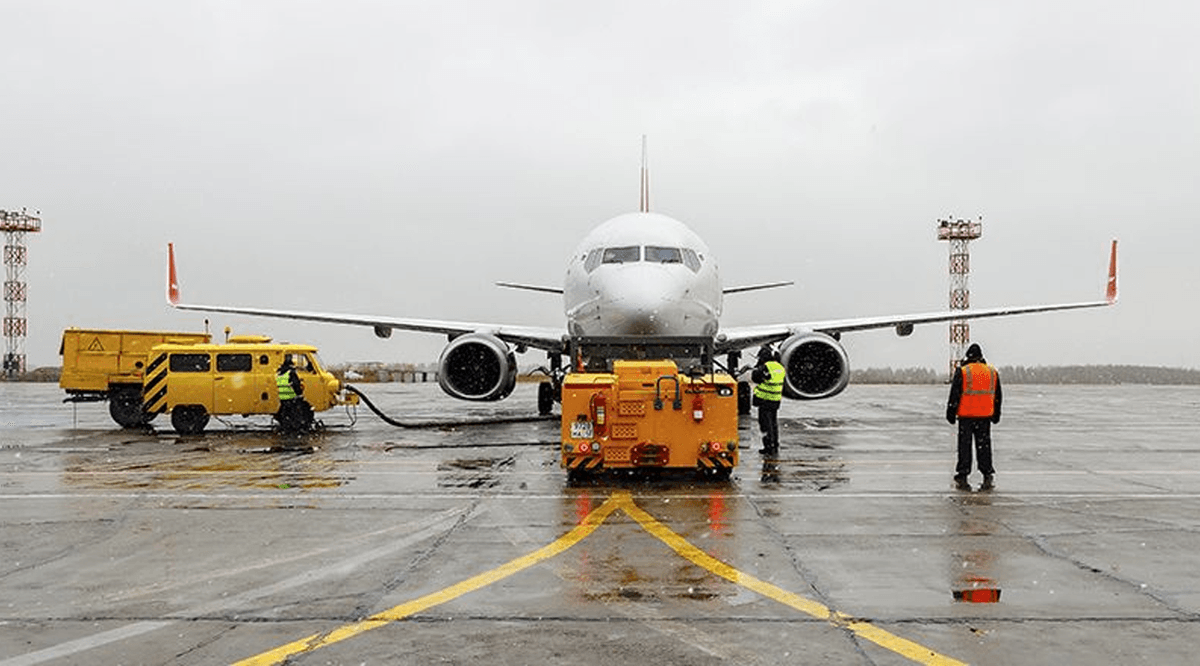

Proper installation and setup of the Aviation Cabin Heating Machine are crucial to ensure its effective and safe operation. Here are the key steps involved in installing and setting up the machine:
- Site Selection: The first step is to select a suitable location for the Aviation Cabin Heating Machine. For stationary models, this should be a fixed position near the aircraft's gate or maintenance area, with easy access to the aircraft's cabin connection points. For portable models, the machine should be placed on a flat, stable surface near the aircraft, ensuring that there is sufficient space for the hoses and ducts to reach the cabin.
- Power Source Connection: Depending on the type of machine, connect it to the appropriate power source. For fuel-powered machines, ensure that the fuel tank is filled with the correct type of fuel (diesel or gasoline) and that the fuel line is properly connected. For electric-powered machines, connect the power cord to a reliable electrical outlet or generator, ensuring that the voltage and amperage match the machine's requirements.
- Hose and Duct Connection: Connect the machine's hoses or ducts to the aircraft's cabin heating inlet. This inlet is typically located on the exterior of the aircraft, near the main door or cargo hold. Ensure that the connection is secure and airtight to prevent heat loss and ensure efficient air distribution. Follow the aircraft manufacturer's guidelines for connecting external heating equipment to avoid damaging the aircraft.
- Exhaust System Setup: For fuel-powered machines, ensure that the exhaust system is properly positioned to direct exhaust gases away from the aircraft, passengers, and ground crew. The exhaust pipe should be extended if necessary to avoid any risk of carbon monoxide exposure. Never operate a fuel-powered Aviation Cabin Heating Machine in an enclosed space without proper ventilation.
- Temperature Setting: Set the desired cabin temperature on the machine's control panel. Refer to the aircraft's specifications and external weather conditions to determine the appropriate temperature. Most machines allow for easy adjustment of the temperature, with digital displays showing the current and set temperatures.
- Safety Checks: Before starting the machine, perform a series of safety checks. Inspect the hoses and ducts for any damage or leaks, ensure that the exhaust system is properly connected and vented, and check that all safety features (such as overheat protection and flame sensors) are functioning correctly. Also, ensure that there are no flammable materials near the machine or the aircraft's cabin inlet.
- Startup and Testing: Start the Aviation Cabin Heating Machine and allow it to run for a few minutes to ensure that it is operating correctly. Check that warm air is being delivered to the cabin and that the temperature is rising to the set level. Monitor the machine for any unusual noises, vibrations, or odors, which may indicate a malfunction. If any issues are detected, shut down the machine immediately and address the problem before restarting.
Maintenance and Servicing of Aviation Cabin Heating Machine
Regular maintenance and servicing are essential to keep the Aviation Cabin Heating Machine in good working order, ensuring reliable performance and extending its lifespan. Here are the key maintenance tasks that should be performed:
- Daily Inspections: Before each use, perform a visual inspection of the machine. Check for any signs of damage, such as cracks in the hoses or ducts, loose connections, or corrosion on the exterior. Inspect the fuel tank (for fuel-powered machines) to ensure that it is properly filled and that there are no leaks. Check the air intake and exhaust systems for any blockages, such as debris or ice.
- Filter Cleaning/Replacement: The machine's air filters prevent dust, dirt, and other contaminants from entering the heating system and the aircraft cabin. These filters should be cleaned or replaced regularly, depending on the operating conditions. In dusty or dirty environments, filters may need to be cleaned more frequently. A clogged filter can reduce heating efficiency and damage the machine's components.
- Fuel System Maintenance: For fuel-powered machines, the fuel system requires regular maintenance. This includes draining any water or sediment from the fuel tank, inspecting the fuel lines and filters for blockages or leaks, and replacing the fuel filter according to the manufacturer's recommendations. Using clean, high-quality fuel is also important to prevent fuel system damage.
- Heating Element Inspection: The heating element is a critical component of the Aviation Cabin Heating Machine. It should be inspected regularly for signs of wear, damage, or corrosion. If the heating element is damaged, it should be replaced immediately to ensure proper heating performance. For electric-powered machines, check the electrical connections to the heating element for tightness and corrosion.
- Temperature Control System Calibration: The temperature control system, including the thermostat and sensors, should be calibrated regularly to ensure accurate temperature readings and control. This involves comparing the machine's temperature readings to a calibrated thermometer and adjusting the system if necessary. Calibration should be performed at least once a year or more frequently if the machine is used in extreme conditions.
- Exhaust System Inspection: For fuel-powered machines, the exhaust system should be inspected for leaks, corrosion, or damage. A leaking exhaust system can release harmful gases, such as carbon monoxide, posing a safety risk. Ensure that the exhaust pipe is securely attached and that there are no cracks or holes. Replace any damaged components immediately.
- Lubrication: Moving parts of the machine, such as fans and pumps, should be lubricated regularly to reduce friction and wear. Use the type of lubricant recommended by the manufacturer and follow the specified lubrication schedule.
- Professional Servicing: In addition to regular maintenance tasks, the Aviation Cabin Heating Machine should be serviced by a qualified professional at least once a year. Professional servicing includes a comprehensive inspection of all components, testing of safety features, and replacement of worn or damaged parts. This helps identify potential issues before they become major problems, ensuring the machine's reliability and safety.
- Record Keeping:Detailed records of all maintenance and servicing activities should be kept for the Aviation Cabin Heating Machine. This includes dates of inspections, filter replacements, fuel system maintenance, heating element inspections, and professional servicing. Records should also include any issues detected, repairs performed, and parts replaced. These records help track the machine's maintenance history, identify patterns of wear or malfunction, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. They also provide valuable information for troubleshooting future problems and planning for replacement or upgrades.

Common Challenges in Using Aviation Cabin Heating Machine
While the Aviation Cabin Heating Machine is a reliable piece of equipment, it can face several challenges during operation. Here are some of the most common challenges:
- Extreme Weather Conditions: Operating the Aviation Cabin Heating Machine in extreme cold, heavy snow, or strong winds can affect its performance. Cold temperatures can reduce the efficiency of the heating element, while snow and ice can block the air intake or exhaust systems. Strong winds can disrupt the distribution of warm air, leading to uneven heating in the cabin.
- Fuel Supply Issues: For fuel-powered machines, fuel supply problems can arise, such as fuel contamination, fuel line freezing, or running out of fuel during extended use. Contaminated fuel can damage the heating element and fuel system components, while frozen fuel lines can prevent the machine from operating altogether.
- Electrical Problems: Electric-powered Aviation Cabin Heating Machines can experience electrical issues, such as power outages, voltage fluctuations, or damaged power cords. These problems can cause the machine to shut down unexpectedly, leaving the cabin without heat.
- Compatibility Issues: Using an Aviation Cabin Heating Machine that is not compatible with the aircraft type can lead to inefficient heating, damage to the aircraft's heating inlet, or unsafe operation. This is particularly common when using portable machines with a diverse fleet of aircraft.
- Maintenance Neglect: Failure to perform regular maintenance can lead to a range of problems, including reduced heating efficiency, increased fuel consumption, and safety hazards. A poorly maintained machine is more likely to break down during critical operations, causing delays and discomfort for passengers.
- Operator Error: Incorrect setup or operation of the Aviation Cabin Heating Machine can lead to suboptimal performance or safety risks. For example, improper connection of hoses or ducts can result in heat loss, while failure to properly vent exhaust gases can lead to carbon monoxide exposure.
Strategies to Overcome Challenges with Aviation Cabin Heating Machine
Addressing the challenges faced by the Aviation Cabin Heating Machine requires proactive measures and effective strategies. Here are some solutions to overcome common challenges:
- Prepare for Extreme Weather: To handle extreme weather conditions, ensure that the Aviation Cabin Heating Machine is equipped with features designed for harsh environments, such as heated air intakes to prevent ice buildup, and wind shields to protect the machine and improve air distribution. Regularly clear snow and ice from the machine and its surroundings during winter operations. For extremely cold temperatures, consider using a machine with a higher heating capacity to compensate for heat loss.
- Ensure Reliable Fuel Supply: For fuel-powered machines, use clean, high-quality fuel and store it in properly insulated tanks to prevent freezing. Install fuel filters to remove contaminants and drain water from the fuel system regularly. Keep extra fuel on hand during extended ground stops to avoid running out of fuel. In cold climates, use winter-grade fuel that is less likely to freeze.
- Stabilize Electrical Supply: For electric-powered machines, connect them to a reliable power source with surge protection to prevent damage from voltage fluctuations. Use backup generators in areas with frequent power outages to ensure continuous operation. Inspect power cords regularly for damage and replace them immediately if any issues are found.
- Verify Compatibility: Before using an Aviation Cabin Heating Machine with an aircraft, verify that it is compatible with the aircraft type. Consult the aircraft manufacturer's specifications and the machine manufacturer's compatibility charts. Train operators to recognize compatibility issues and ensure that the correct machine is used for each aircraft.
- Prioritize Regular Maintenance: Establish a strict maintenance schedule and ensure that all maintenance tasks are performed on time. Train maintenance personnel to properly inspect, clean, and repair the Aviation Cabin Heating Machine. Use diagnostic tools to identify potential issues before they become major problems. Keeping detailed maintenance records can help track the machine's performance and plan for maintenance proactively.
- Train Operators Thoroughly: Provide comprehensive training to operators on the proper setup, operation, and safety procedures for the Aviation Cabin Heating Machine. Include hands-on training to ensure that operators can correctly connect hoses and ducts, set the temperature, and perform safety checks. Regular refresher training can help keep operators up-to-date on best practices and new features of the machine.
Case Studies: Successful Use of Aviation Cabin Heating Machine
Real-world case studies demonstrate the effectiveness of the Aviation Cabin Heating Machine in ensuring passenger comfort and operational efficiency during ground stops. Here are a few examples:
- Major Airline in Cold Climate: A major airline operating in a region with harsh winters faced frequent complaints from passengers about cold cabins during ground stops. The airline invested in a fleet of diesel-powered Aviation Cabin Heating Machines with high heating capacity and heated air intakes. During the first winter after implementation, passenger complaints about cold cabins decreased by 80%. The machines kept the cabins at a comfortable temperature even in temperatures as low as -20°C (-4°F), reducing boarding delays and improving on-time performance by 15%.
- Regional Airport with Diverse Fleet: A regional airport with a diverse fleet of small and medium-sized aircraft struggled with compatibility issues between its existing Aviation Cabin Heating Machines and some of the aircraft. The airport replaced its old machines with a range of portable, hybrid Aviation Cabin Heating Machines that could be adapted to different aircraft types. The new machines were compatible with all aircraft in the fleet, improving heating efficiency and reducing damage to aircraft components. The airport also reported a 25% reduction in fuel consumption due to the hybrid machines' ability to switch to electric power when available.
- International Airport with Strict Emission Regulations: An international airport in a city with strict emission regulations needed to reduce the environmental impact of its ground operations. The airport replaced its fuel-powered Aviation Cabin Heating Machines with electric-powered models. The new machines produced zero emissions, helping the airport meet its sustainability targets. They also operated more quietly, reducing noise pollution around the terminal. Passenger satisfaction scores for cabin comfort during ground stops increased by 30%, and the airport saved on fuel costs.

Future Trends in Aviation Cabin Heating Machine Technology
The Aviation Cabin Heating Machine technology is continuously evolving to meet the changing needs of the aviation industry, with a focus on efficiency, sustainability, and passenger comfort. Here are some key future trends:
- Increased Use of Electric and Hybrid Models: As the aviation industry moves toward sustainability, there will be a growing shift toward electric and hybrid Aviation Cabin Heating Machines. Electric models produce zero emissions, while hybrid models allow for reduced fuel consumption by using electricity when available. Advances in battery technology will make portable electric machines more powerful and longer-lasting, expanding their use in remote locations.
- Smart Temperature Control: Future Aviation Cabin Heating Machines will feature advanced smart temperature control systems using artificial intelligence (AI) and Internet of Things (IoT) technology. These systems will monitor the cabin temperature in real-time, adjust the heating output automatically, and even predict temperature changes based on external conditions and aircraft occupancy. This will ensure optimal comfort while reducing energy consumption.
- Improved Energy Efficiency: Manufacturers will continue to develop more energy-efficient Aviation Cabin Heating Machines by using advanced heating elements, better insulation, and optimized air distribution systems. This will reduce fuel consumption for fuel-powered models and electricity usage for electric models, lowering operating costs and environmental impact.
- Enhanced Connectivity and Monitoring: Future machines will be equipped with enhanced connectivity features, allowing them to be monitored and controlled remotely via a central system. This will enable airport operators to track the performance of each machine, receive alerts for maintenance or malfunctions, and adjust settings from a distance. Remote monitoring can improve operational efficiency and reduce downtime.
- Integration with Aircraft Systems: Some Aviation Cabin Heating Machines may eventually be integrated with the aircraft's own systems, allowing for seamless communication and coordination. For example, the machine could receive data from the aircraft's sensors to adjust heating based on the number of passengers or the cabin's insulation properties, further improving efficiency and comfort.
- Lightweight and Compact Design: Advances in materials and engineering will lead to lighter and more compact Aviation Cabin Heating Machines, making them easier to transport and store. This is particularly beneficial for portable models, which will be more maneuverable and require less storage space.
Choosing the Right Aviation Cabin Heating Machine Provider
Selecting the right provider for the Aviation Cabin Heating Machine is crucial to ensure that you get a high-quality, reliable product that meets your specific needs. Here are key factors to consider when choosing a provider:
- Industry Experience: Look for a provider with extensive experience in manufacturing and supplying Aviation Cabin Heating Machines to the aviation industry. An experienced provider will have a deep understanding of the unique requirements and challenges of airport operations and can offer solutions tailored to your needs.
- Product Quality and Reliability: The provider should offer high-quality machines that are built to last and perform reliably in harsh airport environments. Look for machines that meet international standards and have a proven track record of performance. Ask for references from other airlines or airports that have used the provider's products.
- Range of Products: Choose a provider that offers a wide range of Aviation Cabin Heating Machines, including different power sources, sizes, and capacities. This allows you to select the machine that best fits your fleet of aircraft and operating conditions. A provider with a diverse product line is also more likely to have a solution for any future needs.
- Customization Options: If you have specific requirements, look for a provider that offers customization options. This may include modifying the machine's heating capacity, adding special features, or adapting it to work with specific aircraft types. Customization ensures that the machine meets your exact needs.
- Technical Support and Service: A good provider should offer comprehensive technical support and after-sales service. This includes assistance with installation, training for operators and maintenance personnel, and prompt repair services. Look for a provider with a network of service technicians available to respond quickly to issues, minimizing downtime.
- Warranty and Guarantee: Ensure that the provider offers a comprehensive warranty on their Aviation Cabin Heating Machines. A warranty provides peace of mind that the provider stands behind their product and will repair or replace any defective components. Ask about the warranty terms, including the duration and coverage.
- Price and Value: While price is an important factor, it should not be the sole consideration. Compare the price of the machine with its quality, features, and reliability to determine the best value. A slightly higher price for a high-quality machine may be worth it in the long run due to lower maintenance costs and longer lifespan.

Conclusion: Aviation Cabin Heating Machine as a Vital Asset for Airports and Airlines
The Aviation Cabin Heating Machine is a vital asset for airports and airlines, ensuring that aircraft cabins remain warm and comfortable during ground stops, even in the harshest weather conditions. Its role in maintaining passenger comfort, protecting passenger and crew safety, and ensuring operational efficiency cannot be overstated.
From diesel-powered models for large aircraft in cold climates to electric-powered machines for environmentally conscious operations, the Aviation Cabin Heating Machine comes in a variety of types to meet different needs. With key features such as high heating capacity, precise temperature control, and durable construction, these machines provide reliable performance in the challenging airport environment.
By addressing common challenges through proper maintenance, operator training, and the use of appropriate technology, airports and airlines can maximize the effectiveness of the Aviation Cabin Heating Machine. The future of this technology looks promising, with advancements in sustainability, smart control, and connectivity set to further improve performance and efficiency.
Choosing the right provider is essential to ensuring that you get a high-quality Aviation Cabin Heating Machine that meets your specific needs. With the right machine and proper operation, airports and airlines can enhance the passenger experience, improve operational efficiency, and comply with regulatory standards, making the Aviation Cabin Heating Machine an indispensable part of modern aviation operations.

