Introduction

In the bustling world of aviation, Ground Power Units (GPUs) play a pivotal role in ensuring that aircraft are ready for takeoff without a hitch. These unsung heroes provide the necessary power to support various systems when an aircraft is on the ground, eliminating the need for engines to run unnecessarily. Understanding what an aircraft GPU does is crucial for anyone involved in airport operations or maintenance.
The Importance of Ground Power Units
Ground Power Units are essential for modern aviation, serving as a reliable source of electrical power during ground operations. Without GPUs, airlines would face significant delays and increased operational costs due to reliance on Auxiliary Power Units (APUs) or running engines solely for power needs. By providing efficient energy solutions, GPUs contribute to smoother airport operations and reduced environmental impact.
Understanding Aircraft Power Needs
Aircraft have diverse power requirements that must be met while they are parked at gates or during maintenance checks. From powering onboard systems like lighting and avionics to supporting engine start-up processes, understanding these needs is vital for effective ground handling. This knowledge not only helps in selecting the right GPU but also informs decisions related to aircraft GPU price considerations.
Overview of GPU Functionality
A GPU serves multiple functions by supplying electrical energy and pneumatic pressure necessary for starting turbine engines and operating essential systems while on the ground. It acts as a bridge between airport infrastructure and aircraft capabilities, ensuring that planes can be serviced efficiently without consuming fuel unnecessarily. With advancements in technology, today's GPUs are more powerful and versatile than ever, making them indispensable tools in aviation operations.
What is a GPU on an aircraft?

When talking about aircraft power systems, the Ground Power Unit (GPU) is a crucial player in ensuring that an aircraft can operate efficiently while on the ground. Essentially, a GPU provides the necessary electrical power and pneumatic pressure to support various aircraft functions before takeoff or after landing. This means that without a reliable GPU, pilots and ground crews would face significant challenges in preparing an aircraft for flight.
Definition and Purpose
A GPU, or Ground Power Unit, is designed to supply external electrical power to an aircraft while it is parked at the gate or on the tarmac. The primary purpose of this unit is to power essential systems such as lighting, avionics, and environmental controls without relying on the aircraft's internal batteries or Auxiliary Power Unit (APU). By using a GPU, airlines can conserve fuel and reduce emissions during ground operations—talk about being eco-friendly!
Key Components of an Aircraft GPU
An aircraft GPU consists of several key components that work together to deliver power effectively. These include a generator set for producing electricity, control panels for monitoring output and performance, connectors compatible with various aircraft types, and safety features like circuit breakers to prevent overloads. The combination of these components ensures that the GPU can meet diverse power requirements across different models of commercial and private jets.
Types of GPUs in Aviation
There are several types of GPUs used in aviation today, each tailored for specific operational needs. Generally classified into two main categories—mobile GPUs and stationary GPUs—these units can be found at airports worldwide. Mobile GPUs are often preferred for their flexibility in moving between different parking spots while stationary units provide consistent performance at fixed locations; both play vital roles in supporting efficient airport operations.
What is the difference between GPU and APU in aviation?

In the world of aviation, understanding the difference between a Ground Power Unit (GPU) and an Auxiliary Power Unit (APU) is crucial for efficient aircraft operations. Both serve essential roles but cater to different needs during ground handling. While an aircraft GPU provides electrical power and air conditioning when parked, an APU generates power for various systems when the aircraft is in motion or during flight preparation.
Distinct Functions Explained
The primary function of an aircraft GPU is to supply electrical power to the aircraft while it is on the ground, ensuring that systems such as lighting, avionics, and climate control are operational without relying on the main engines. Conversely, an APU serves multiple purposes; it not only provides electrical power but also supplies bleed air for engine start-up and cabin conditioning during taxiing or while parked. This distinction highlights that while both units support power requirements, their applications differ significantly based on operational needs.
When to Use GPU vs. APU
Choosing between a GPU and an APU often depends on specific operational scenarios. If you’re at a busy airport where quick turnarounds are essential, using a GPU can be more efficient since it allows engines to remain off while still powering necessary systems. However, if you're in remote locations or need bleed air for starting turbine engines or running auxiliary systems, then relying on an APU becomes indispensable.
Pros and Cons of Each System
Both systems have their advantages and drawbacks that operators should consider carefully when evaluating options like aircraft GPU price or manufacturer reliability. The benefits of using a GPU include lower fuel consumption since engines aren’t running, reduced noise pollution at airports, and lower maintenance costs compared to APUs. On the flip side, APUs offer versatility by powering up essential functions even away from ground support infrastructure but come with higher operational costs due to fuel use and maintenance requirements.
What is the main purpose of the GPU for turbine engines?

Ground Power Units (GPUs) play a crucial role in supporting turbine engines, ensuring that aircraft are ready for takeoff without relying solely on onboard power. The primary purposes of an aircraft GPU include assisting with engine start-up, powering essential systems while on the ground, and enhancing overall operational efficiency and safety. Understanding these functions helps clarify why GPUs are indispensable in modern aviation.
Supporting Engine Start-Up
One of the most critical roles of an aircraft GPU is to provide the necessary electrical power to initiate engine start-up procedures for turbine engines. When pilots prepare for departure, they rely on the GPU to deliver consistent voltage and current, which is vital for starting engine systems efficiently. Without this support from a GPU, starting an aircraft’s turbine engine would be far more challenging and could lead to increased wear or even failure.
Powering Aircraft Systems While on Ground
While parked at the gate or during maintenance checks, aircraft require power for various systems such as lighting, avionics, and environmental controls. An aircraft GPU supplies this essential energy without needing to run the auxiliary power unit (APU), which can save fuel and reduce emissions during ground operations. By using a GPU instead of relying solely on onboard resources, airlines can optimize their operational costs while ensuring passenger comfort.
Enhancing Efficiency and Safety
By providing immediate access to electrical power without taxing onboard systems, GPUs help streamline pre-flight checks and maintenance tasks—ultimately leading to quicker turnaround times for flights. Additionally, having a reliable external power source minimizes risks associated with engine idling or unnecessary APU usage that could pose safety hazards.
How to connect GPU to aircraft?
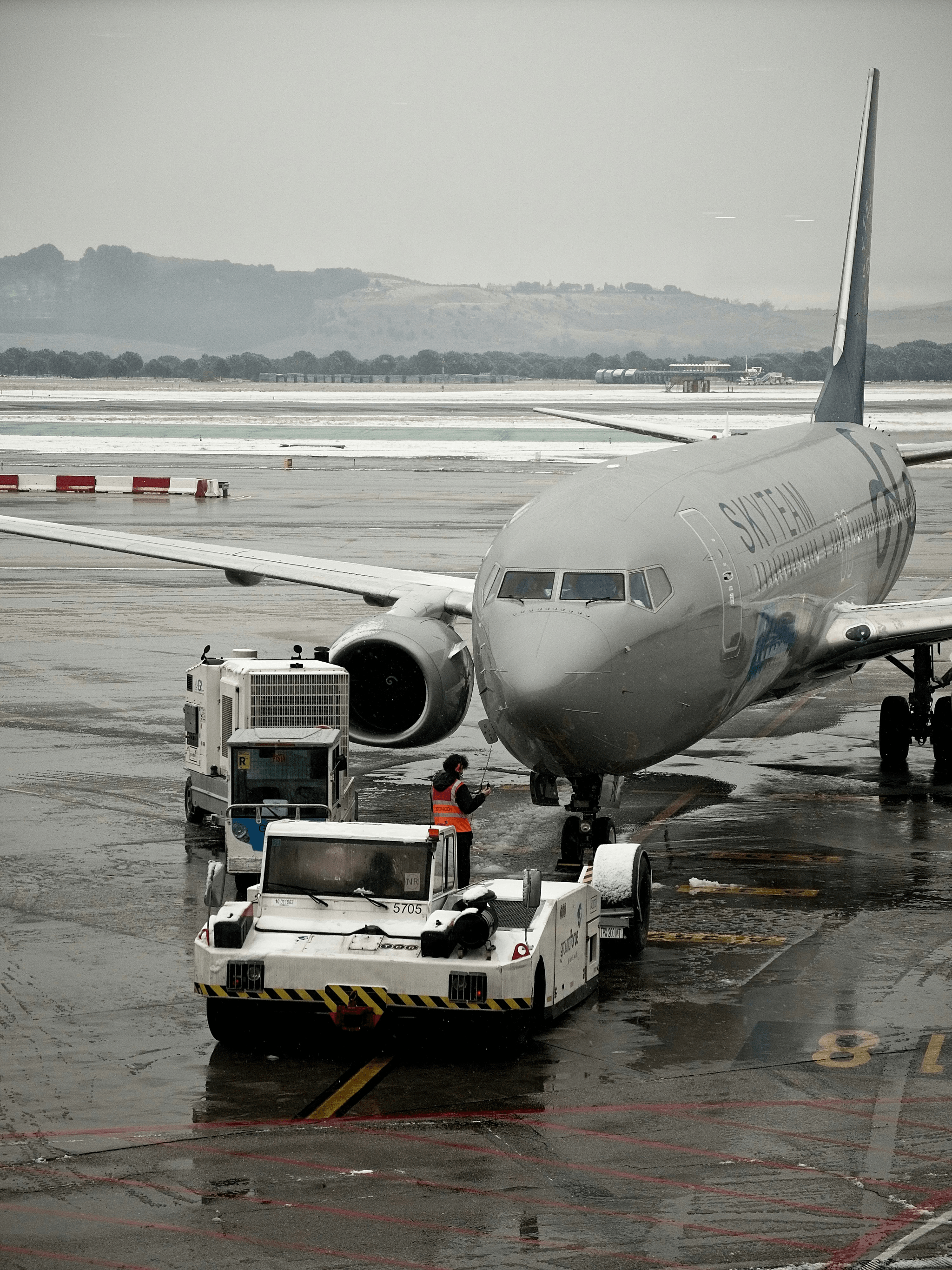
Connecting a Ground Power Unit (GPU) to an aircraft is a crucial process that ensures the aircraft receives the necessary power while on the ground. This procedure requires careful attention to detail and adherence to safety protocols, as improper connections can lead to equipment damage or safety hazards. Understanding how to connect a GPU correctly not only enhances operational efficiency but also prolongs the life of both the GPU and the aircraft systems it powers.
Step-by-Step Connection Process
To begin connecting the aircraft GPU, first ensure that both the GPU and the aircraft are parked in a safe area with adequate space for maneuvering. Next, turn off all power sources on the aircraft before approaching with the GPU cables. Once you’ve confirmed that everything is powered down, locate the appropriate power receptacles on both devices; this is often specified in What is a GPU on an aircraft? manuals.
After identifying connection points, carefully align and insert the GPU connectors into their respective sockets on the aircraft. It’s essential to listen for any clicks or indicators that confirm secure connections have been made. Finally, switch on the GPU power supply, monitor readings for any irregularities, and ensure all systems are functioning properly before beginning any engine start-up procedures.
Safety Measures During Connection
Safety should always be your top priority when connecting an aircraft GPU. Before initiating any connection process, wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves and safety goggles to protect against electrical hazards. Additionally, ensure that all personnel in proximity are aware of what you’re doing; communication is key when dealing with potentially dangerous equipment.
Always double-check voltage settings on your GPU before connecting it to an aircraft; mismatched voltages can lead not only to equipment failure but also create hazardous situations for ground crew members. Moreover, make sure there are no loose cables or obstructions around your work area that could cause tripping or accidental disconnections during operation. By following these safety measures diligently, you can mitigate risks associated with using GPUs in aviation.
Common Connection Issues
While connecting an aircraft GPU is generally straightforward, various common issues may arise during this process which could disrupt operations if not addressed promptly. One frequent problem involves incompatible connectors; ensuring compatibility between different types of GPUs and various aircraft models is crucial—this relates back to understanding What is a GPU on an aircraft? specifications fully.
Another issue might be insufficient power output from older GPUs due to wear or malfunctioning components; always check performance indicators before attempting connection so you don’t end up facing unexpected outages mid-operation! Lastly, watch out for cable damage or fraying which can lead not only to inefficient power transfer but also present serious safety risks—regular inspections of your equipment will help avoid these frustrating scenarios.
Aircraft GPU Manufacturers You Should Know

In the world of aviation, selecting the right aircraft GPU manufacturers can significantly impact the efficiency and reliability of ground operations. With a variety of brands offering specialized solutions, understanding who the key players are is essential for any operator looking to invest in an aircraft GPU. This section highlights leading brands, their innovative technologies, and the standards that guide their production.
A Look at Leading Brands
When it comes to aircraft GPUs, several manufacturers stand out for their quality and performance. Companies like Hobart Ground Power, JBT AeroTech, and Powervamp have built reputations for producing reliable ground power units tailored to meet diverse aviation needs. Each brand offers unique features in their products that cater to different types of aircraft and operational requirements.
For instance, Hobart Ground Power is known for its robust designs that ensure longevity even under heavy use. Meanwhile, JBT AeroTech focuses on integrating advanced technology into their GPUs to enhance usability and efficiency. Understanding these leading brands can help operators make informed decisions about which aircraft GPU best suits their operational needs.
Innovative Technologies by Major Manufacturers
The landscape of aircraft GPUs is evolving rapidly with innovative technologies being introduced by major manufacturers. For example, some manufacturers are now offering hybrid or fully electric GPUs that reduce emissions while providing substantial power output. This shift not only supports environmental goals but also enhances fuel efficiency when considering What is the main purpose of the GPU for turbine engines?
Additionally, advancements in digital monitoring systems allow operators to keep track of power consumption and system performance in real-time. These innovations streamline ground operations and minimize downtime during critical phases such as engine start-up or powering auxiliary systems while parked on the tarmac—key aspects highlighted when discussing How to connect GPU to aircraft?
Industry Standards and Regulations
Navigating through industry standards and regulations is crucial when selecting an aircraft GPU manufacturer. Compliance with international aviation regulations ensures that GPUs meet safety requirements while delivering reliable performance across various environments. Organizations such as the International Air Transport Association (IATA) set guidelines that influence how manufacturers design their products.
Moreover, understanding these standards helps operators evaluate potential suppliers based on safety certifications and operational efficiencies they provide—critical considerations when analyzing What is the difference between GPU and APU in aviation? By adhering to established norms, manufacturers contribute positively towards enhancing overall safety within airport operations.
Haisen's Ground Support Unit Overview

Haisen's Ground Support Unit, particularly the YC160DT GPU, stands out in the competitive landscape of aircraft GPUs. This unit is designed to efficiently meet the power requirements of various aircraft while on the ground, ensuring smooth operations and enhanced safety. With a focus on reliability and performance, Haisen’s GPU is an essential tool for modern aviation.
Features of the YC160DT GPU
The YC160DT GPU boasts several impressive features that cater to diverse aviation needs. Primarily, it offers a robust power output that can support various aircraft types, making it versatile for different airport operations. Additionally, its compact design allows for easy maneuverability around crowded tarmacs without sacrificing functionality.
Another notable feature of this aircraft GPU is its user-friendly interface that simplifies operation for ground crew members. With clear indicators and controls, personnel can quickly assess power levels and operational status. Furthermore, advanced safety mechanisms are integrated into the system to prevent overloading or short-circuiting during use.
Lastly, the YC160DT is equipped with noise-reduction technology that minimizes operational sound levels—an essential consideration at busy airports where noise regulations are strict. This feature not only enhances comfort for personnel but also aligns with environmental standards in aviation today.
Performance Capabilities and Specifications
When evaluating performance capabilities and specifications of the YC160DT GPU, several key metrics come into play. This unit provides a steady output voltage tailored to meet specific aircraft needs—crucial for supporting engine start-up processes as well as powering onboard systems while on the ground. Its reliable power supply ensures that all necessary equipment functions efficiently without interruption.
In terms of specifications, this aircraft GPU typically delivers between 28V DC to 400Hz AC output options—allowing compatibility with a wide range of turbine engines and other electrical systems found in modern planes. Moreover, its ability to operate effectively under varying weather conditions makes it an ideal choice for airports located in diverse climates.
Haisen has also ensured that maintenance requirements are kept minimal; with durable materials used throughout construction and intuitive design elements allowing easy access to critical components when servicing is needed. This commitment to quality translates into reduced downtime and lower overall costs associated with maintaining ground support equipment.
Advantages for Airport Operations
One significant advantage of using Haisen's YC160DT Aircraft GPU in airport operations lies in its efficiency during turnarounds—reducing time spent on ground handling tasks significantly compared to older models or alternative systems like APUs (Auxiliary Power Units). By providing immediate power upon connection, crews can swiftly prepare aircraft for departure without delays caused by insufficient power supply.
Additionally, utilizing a dedicated aircraft GPU helps reduce fuel consumption when compared to relying solely on APUs during ground operations; this translates into cost savings not only from lower fuel expenditure but also from decreased wear-and-tear on turbine engines over time. These financial benefits make investing in high-quality GPUs like Haisen's a smart move for airlines looking to optimize their operational budgets.
Finally, incorporating advanced technology within Haisen’s GPUs enhances overall safety measures at airports by minimizing risks associated with electrical faults or malfunctions during connection processes—addressing concerns outlined earlier regarding how to connect GPUs effectively without compromising safety protocols established within aviation standards.
Conclusion

In summary, understanding the role of aircraft GPUs is essential for anyone involved in aviation, from ground crew to airline management. The aircraft GPU serves as a crucial power source while on the ground, ensuring that all systems function optimally without relying on onboard engines. As we’ve explored, knowing what a GPU is on an aircraft and how it differs from an APU allows for better decision-making when it comes to operational efficiency.
Key Takeaways on Aircraft GPUs
Aircraft GPUs are indispensable for providing electrical power and air conditioning to aircraft during ground operations. They not only support engine start-up but also power various systems while the aircraft is stationary, enhancing both safety and efficiency. With advancements in technology, understanding the different types of GPUs available can help operators choose the best solutions tailored to their specific needs.
Future of Ground Power Units in Aviation
The future of ground power units in aviation looks promising as manufacturers continue to innovate with energy-efficient designs and eco-friendly technologies. As airlines focus more on sustainability, we can expect a shift towards electric and hybrid GPUs that minimize environmental impact while maintaining performance standards. This evolution will likely lead to reduced operational costs and improved reliability across airport operations.
Making Informed Decisions on Aircraft GPU Price
When considering an aircraft GPU price, it’s crucial to evaluate not just the initial cost but also long-term maintenance and operational efficiencies. Researching various aircraft GPU manufacturers will provide insights into quality options available in the market today. Additionally, understanding how to connect a GPU to an aircraft safely ensures that you get the most value out of your investment while keeping safety at the forefront.
